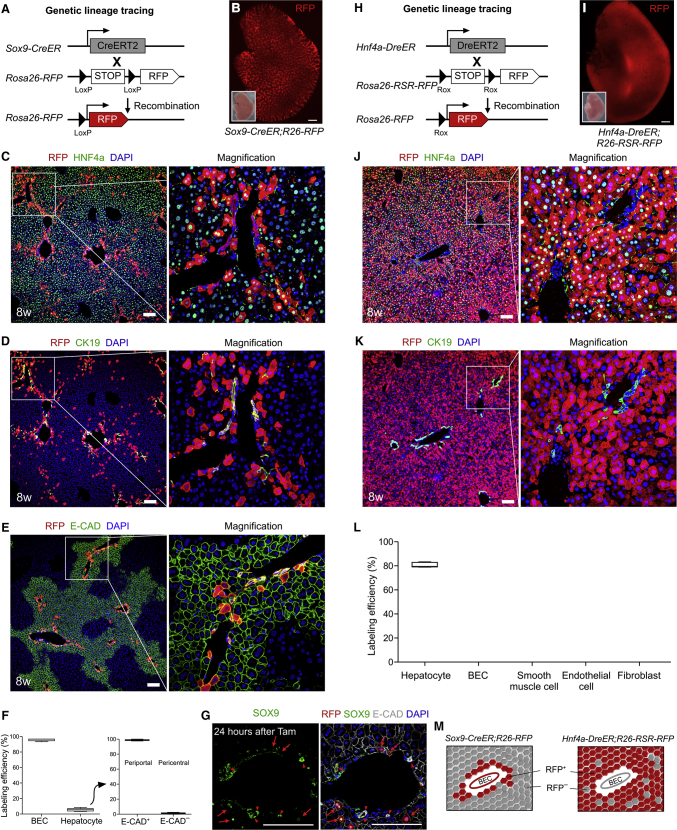
Figure 1.
Fate Mapping of Hepatic Cell Lineages by Sox9-CreER or Hnf4a-DreER
(A and H) Schematic figure showing lineage-tracing strategy by Sox9-CreER;R26-RFP (A) or Hnf4a-DreER;R26-RSR-RFP (H).
(B and I) Whole-mount fluorescence views of livers from 8-week-old adult mice. Tamoxifen was induced 4 days later. Insets indicate bright-field images.
(C and J) Immunostaining for RFP and HNF4a on liver sections.
(D and K) Immunostaining for RFP and CK19 on liver sections.
(E) Immunostaining for RFP and periportal hepatocyte marker E-CAD on liver sections.
(F) Quantification of the percentage of labeled CK19+ biliary epithelial cells (BECs) or HNF4a+ hepatocytes (left panel). The percentage of E-CAD+ or E-CAD- cells in labeled hepatocytes is shown on the right panel. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 5.
(G) Immunostaining for SOX9, RFP, and periportal hepatocyte marker E-CAD on liver sections.
(L) Quantification of the percentage of labeled cells among different lineages. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 5.
(M) Cartoon image showing the fate mapping of hepatic cells by Sox9-CreER or Hnf4a-DreER. Scale bars, 1 mm (B and I) and 100 μm (C–E, G, J, and K).