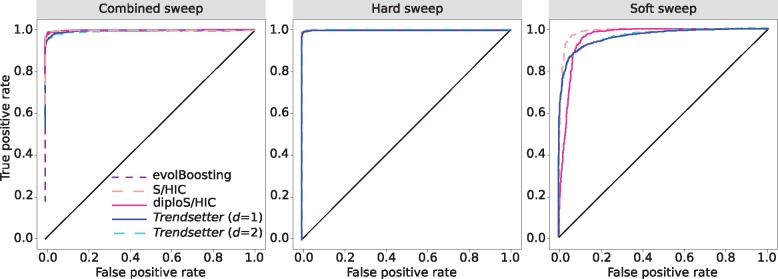
Fig. 3.
Receiver-operating characteristic curves comparing the powers of various methods to distinguish sweeps from neutrality. (Left) Powers to differentiate sweeps from neutrality, by comparing the combined probability of any sweep (hard or soft) under equally mixed hard and soft sweep simulations with the same probability under neutral simulations. (Middle) Powers to differentiate hard sweeps from neutrality, by comparing the probability of a hard sweep under hard sweep simulations with the same probability under neutral simulations. (Right) Powers to differentiate soft sweeps from neutrality, by comparing the probability of a soft sweep under soft sweep simulations with the same probability under neutral simulations. All simulations were performed under a constant-size demographic history with selection coefficients for sweep scenarios drawn uniformly at random on a log scale of . All methods were trained with three classes: neutral, hard sweep, and soft sweep.