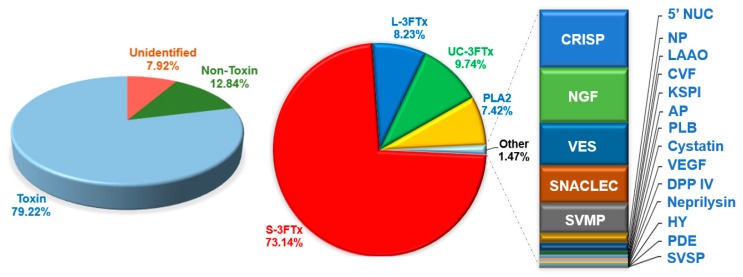
Figure 2.
Relative abundance of transcripts (in percentage of FPKM) expressed in the venom glands of Malaysian Naja sumatrana. Toxin transcripts dominate the overall expression (79.22%). Within toxin transcripts, three-finger toxin (3FTx) is the most abundantly expressed toxin family in the venom glands (91.11% of the toxin FPKM). Of these, the short three-finger toxins (S-3FTx) constitute 73.14%, whereas the long three-finger toxins (L-3FTx) constitute 8.23%. Non-conventional three-finger toxins (NC-3FTx) and phospholipases A2 (PLA2) constitute 9.74% and 7.42%, respectively. Abbreviations: S-3FTx, short three-finger toxin; L-3FTx, long three-finger toxin; UC-3FTx, non-conventional three-finger toxin; PLA2, phospholipase A2; CRISP, cysteine-rich secretory protein; NGF, nerve growth factor; VES, vespryn; SNACLEC, snake venom C-type lectin/lectin-like protein; SVMP, snake venom metalloproteinase; 5’NUC, 5’ nucleotidase; NP, natriuretic peptide; LAAO, L-amino acid oxidase; CVF, cobra venom factor; AP, aminopeptidase; PLB, Phospholipase B; KSPI, Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; HY, hyaluronidase; DPP IV, dipeptidylpeptidase IV; PDE, phosphodiesterase; and SVSP, snake venom serine protease.