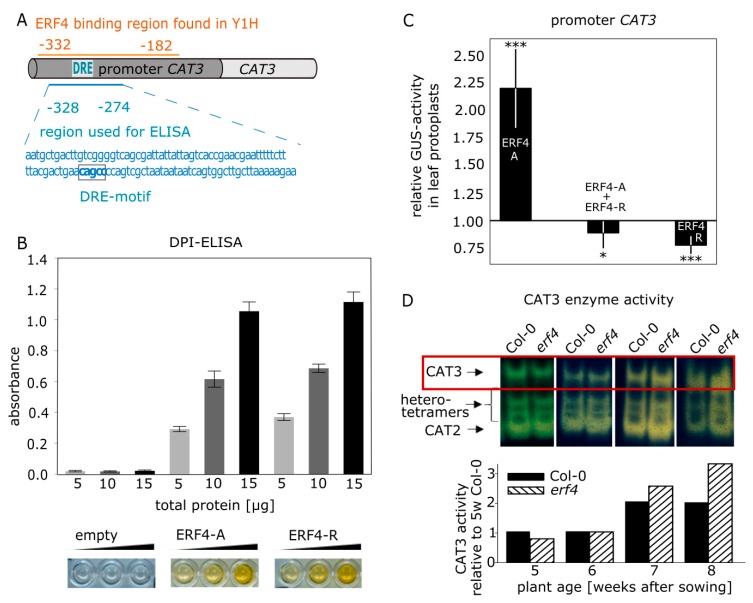
Figure 5.
ERF4 binds to the CATALASE3 promoter and can act as activator and repressor. (A) Schematic representation of the CAT3 promoter fragments used for Y1H screen and for DPI-ELISA. (B) DPI-ELISA using bacterial crude extracts of E. coli BL21 Rosetta cells expressing 6xHis-ERF4-A, 6xHis-ERF4-R or the empty vector and a 55-bp biotinylated DNA fragment of the CAT3 promoter, which contains the DRE motif CAGCC. Representative wells of the micro titer plate are shown below the graph. Yellow color indicates interaction. Error bars indicate ±SE, n = 4–5. (C) Transient expression assays were performed using the 1.8 kbp fragment of the CAT3 promoter upstream of the start codon in Arabidopsis Col-0 and erf4 leaf protoplasts. Values represent fold-change of GUS-activity relative to the empty vector after normalization to luciferase activity to compensate for differences in transformation efficiency. Data are means of seven experiments (n = 7). Statistical differences were analyzed by one sample t-test (* p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.005, *** p ≤ 0.0005). (D) Enzyme activity of catalase isoforms of Col-0 and erf4 mutant plants is visualized on a zymogram. Protein crude extract (10 μg) of leaf No. 6 of 5- to 8-week-old plants were separated on 7.5% native gels and stained for catalase activity. Proteins were extracted of a pool of at least 10 leaves. Intensities of the CAT3 bands were quantified using ImageJ.