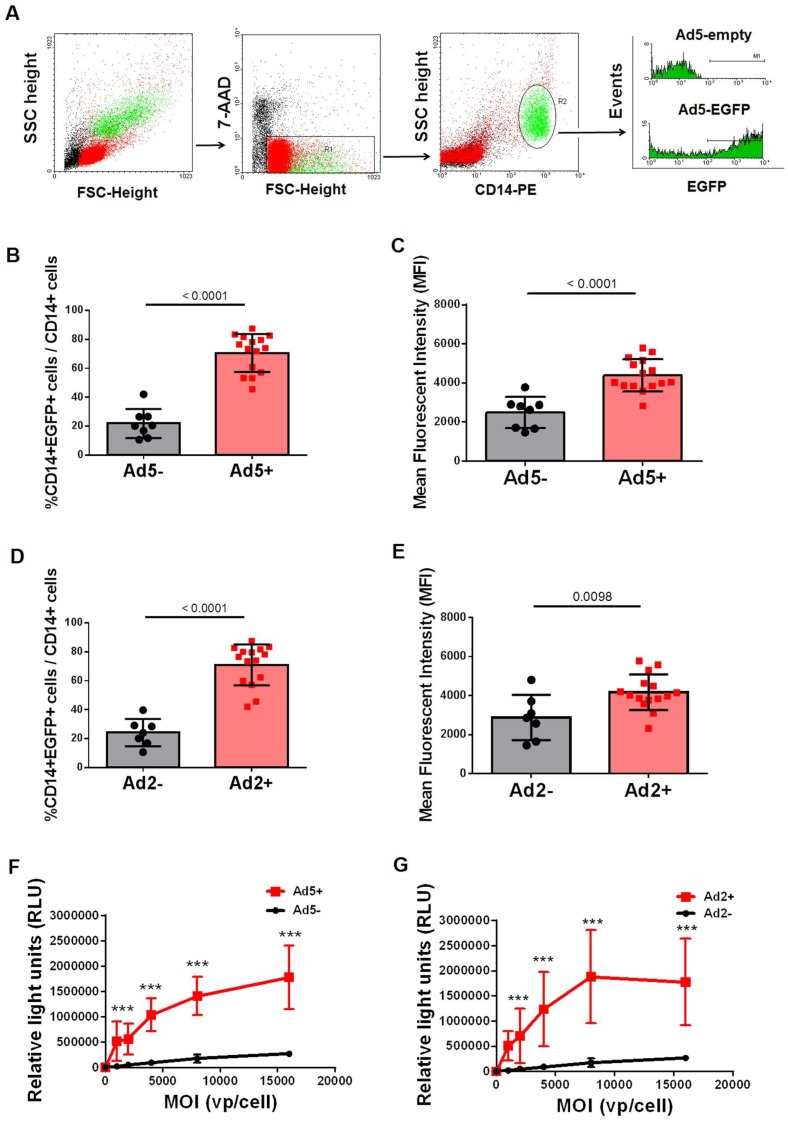
Figure 1.
CD14+ monocytes from Ad-seropositive individuals exhibited an increased susceptibility to Ad infection. (A) Representative graphics of FACS analysis. Human PBMCs were infected with Ad5-EGFP or Ad2-EGFP, and the proportions of EGFP-positive cells in different cell populations were determined by FACS analysis. Herein, EGFP-positive cells represent those cells that have been infected with Ad5 or Ad2. (B) Percentage of EGFP-positive cells in CD14+ cells of Ad seropositive subjects and seronegative subjects after infected with Ad5-EGFP at 1250 vp/cell. (n = 6). (C) Expression level of EGFP protein (represented with MFI value) in CD14+ cells from Ad seropositive subjects and seronegative subjects after infected with Ad5-EGFP at 1250 vp/cell (n = 6). (D) Percentage of EGFP-positive cells in CD14+ cells of Ad seropositive subjects and seronegative subjects after infected with Ad2-EGFP at 1250 vp/cell (n = 6).(E) Expression level of EGFP protein (represented with MFI value) in CD14+ cells from Ad seropositive subjects and seronegative subjects after infected with Ad2-EGFP at 1250 vp/cell (n = 6). (F) Percentage of RLU (Relative light units) in PBMC of Ad seropositive subjects and seronegative subjects after infected with Ad5-SEAP at 0, 1000, 2000, 4000, 8000, and 16,000 vp/cell. (n = 6). (G) Percentage of RLU (Relative light units) in PBMC of Ad seropositive subjects and seronegative subjects after infected with Ad2-SEAP at 0, 1000, 2000, 4000, 8000, and 16,000 vp/cell. (n = 6). The bars represent the standard error. ***: p < 0.001.