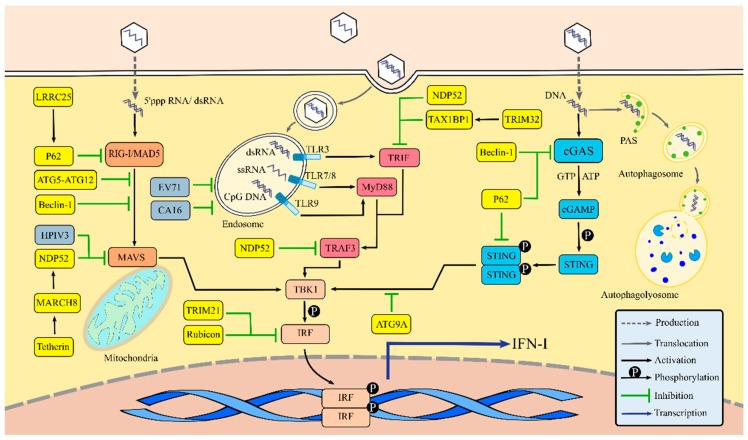
Figure 2.
Autophagy regulates the expression of IFN-I. There are three major pattern recognition receptor (PRR) signaling pathways for regulating IFN-I expression, including the RLRs, TLRs, and cGAS-STING pathways. After recognizing a viral pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP), PRRs recruit downstream signaling molecules, activate signaling cascades via TBK1 and IRF, and ultimately result in the expression of IFN-I. Autophagy can regulate virus detection by degrading viral PAMPs or delivering viral PAMPs to endosomes. Autophagy-related gene (ATG) proteins such as ATG5, ATG9A, ATG12, and Beclin-1 function as regulators of IFN-I production. Selective autophagy mediated by P62, NDP52, and TAX1BP1 plays a vital role in balancing the PRR-mediated IFN-I signaling. Viruses such as HPIV3, EV71, and CA16 can also manipulate key molecules of the autophagic process to inhibit IFN-I production.