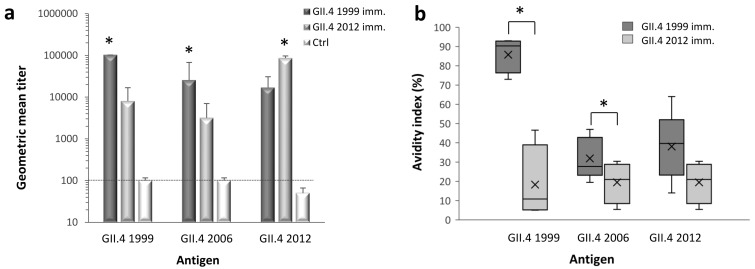
Figure 1.
Titers and avidity of norovirus (NoV) type-specific and cross-reactive serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies. Mice were immunized with GII.4 1999 (5 mice) and GII.4 2012 (4 mice) virus-like particles (VLPs) and the immune sera was used in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to determine the magnitude of IgG antibodies against homologous and heterologous NoV VLPs (a). Serum of mice receiving phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (5 mice) was used as a negative control (Ctrl). Shown are the geometric mean titers (GMTs) with 95% confidence intervals (error bars) counted from individual mice end-point titers in each immunization group. The dashed line illustrates the cut-off titer for samples considered positive. The avidity of IgG antibodies was measured from individual mice sera against homologous and heterologous NoV VLPs (b) as described in the Material and Methods. Horizontal lines in the box plots represent the medians, cross-symbols (×) represent the means, and the boxes illustrate the interquartile range that contains 50% of values with whiskers extending to the highest and lowest values. The antigen-specific antibody titers and the avidity indexes between immunization groups were compared by the Kruskal–Wallis test and significant differences (p value <0.05) are identified with an asterisk (*).