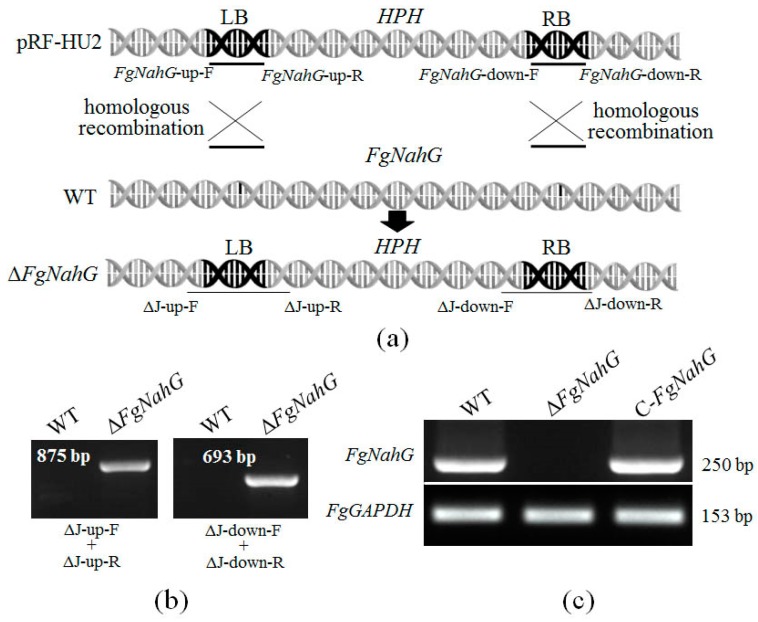
Figure 3.
Construction of FgNahG deletion and complementation mutants. (a) The left border (LB) and right border (RB) were amplified from the wild-type (WT) strain with the FgNahG-up-F/FgNahG-up-R and FgNahG-down-F/FgNahG-down-R primer pairs, respectively, for the subsequent construction of recombinant plasmids. The ΔFgABCC9 mutants were generated by the homologous recombination between the recombinant plasmid and the FgNahG sequence. The bold fragments correspond to the LB and RB of FgNahG. HPH, hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene. (b) Verification of ΔFgNahG by PCR with the ΔJ-up-F/ΔJ-up-R and ΔJ-down-F/ΔJ-down-R primer pairs. (c) Verification of the expression of FgNahG in ΔFgNahG and C-FgNahG strains by RT-PCR with the Rj-FgNahG-F/Rj-FgNahG-R primer pair, which targeted the FgNahG coding region. FgGAPDH was used as a reference gene. All PCR products were verified by sequencing at a commercial company (Qingke, Chengdu, China).