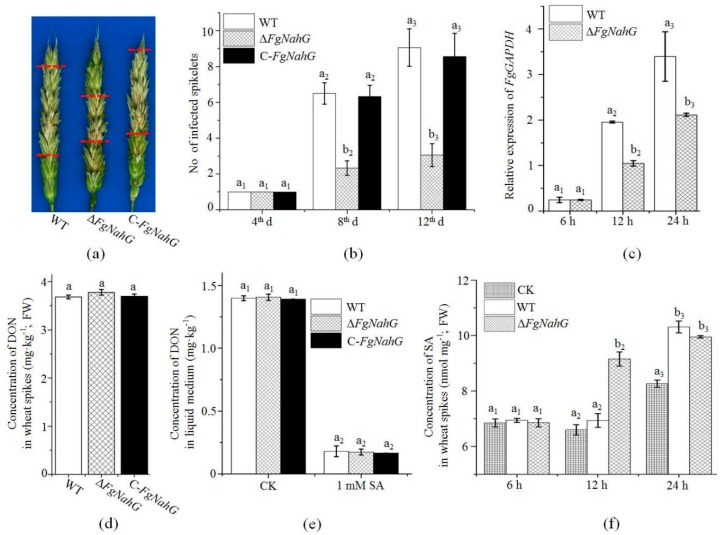
Figure 7.
Effect of FgNahG on F. graminearum pathogenicity in wheat. (a) Head blight symptoms of spikes inoculated with the wild-type (WT), ΔFgNahG or C-FgNahG strains at 12 days after inoculations. Red lines indicate the spread of head blight symptoms in spikes. (b) Numbers of infected and bleached spikelets at 4, 8 and 12 days after inoculations. (c) Relative expression of FgGAPDH in wheat spikes at 6, 12 and 24 h after the initial inoculations. (d) Comparison of deoxynivalenol (DON) contents in wheat spikes inoculated with the WT, ΔFgNahG or C-FgNahG strains at 6 days after inoculations. (e) Measurement of DON production by mycelia grown in liquid medium (the same amount of mycelia was used). The DON production data are provided as mg kg−1 mycelia. (f) Levels of SA in spikes inoculated with water (CK treatment), the WT strain or the ΔFgNahG strain at 6, 12 and 24 h after inoculations. Values are provided as the mean ± standard deviation of three biological replicates per treatment. Different letters above each column indicate significant differences at p ≤ 0.05. FW, fresh weight.