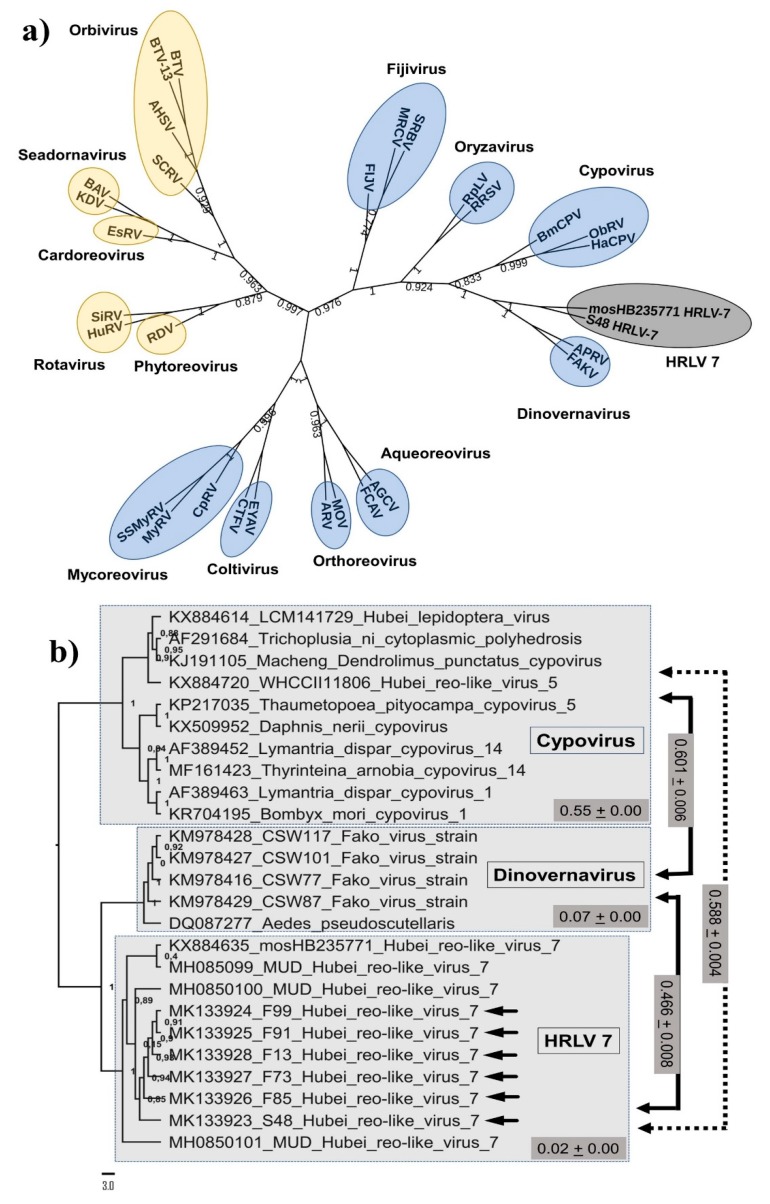
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic trees constructed with the RdRp gene region of reoviruses. (a) Phylogeny of representative reovirus sequences based on the alignment of full-length protein sequences of RdRp. HRLV 7 strains are highlighted in the gray circle. Members of the subfamily Spinareovirinae are highlighted in blue, and members of the subfamily Sedoreovirinae are highlighted in yellow. The various genera are also indicated in bold. Tip labels include the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) abbreviations. This tree was constructed using the Neighbor-Joining method and assuming a JTT model [24]. Values on the node of the trees indicate the statistical support based on a bootstrap test using 1000 replicates. Sequences used for phylogenetic analyses are shown in Supplementary Table S1. (b) Maximum likelihood (ML) tree based on nearly full-length of nucleotide sequences of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRp) shows three groups (gray areas) containing strains from Dinovernavirus, Cypovirus and HRLV 7 strains. The Brazilian strains described in this work are indicated by arrows. The filled gray rectangle indicates genetic distance within and between the clades. The ML tree was inferred using the General Time Reversible (GTR) + gamma distribution model and values on node of the trees indicate the statistical support based on the approximate likelihood ratio test (aLRT).