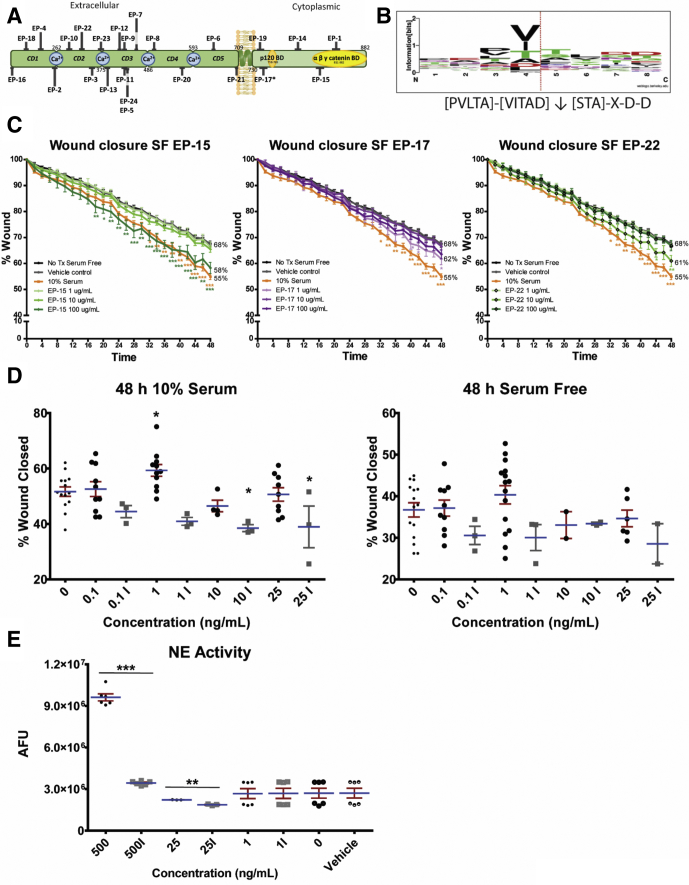
Supplementary Figure 1.
(A) Diagrammatic representation of peptide localizations of human E-cadherin generated by NE in vitro. (B) Sequence logo cleavage sites of E-cadherin by NE as generated by WebLogo Software.1 The height of the amino acid 1-letter code illustrates the relative observed frequency. The dotted red line indicates the NE cleavage site. The local cleavage site residue pattern is [PVLTA]-[VITAD]↓[STA]-X-D-D. (C) E-cadherin peptides (designated EP-15, 17, and 22) significantly and synergistically enhanced healing in scratch-wounded Caco-2 monolayers over 48 hours in the absence of serum. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 compared with vehicle and untreated controls (using a 2-way analysis of variance with the Bonferroni post-test). (D) Low-dose NE enhances wound healing in Caco-2 cells. Purified human NE showed a concentration- and activity-dependent wound-healing effect in scratch-wounded Caco-2 monolayers over 48 hours in the presence of serum (left panel), but not in the absence of serum (right panel). (E) The proteolytic activity of NE was confirmed to be reduced significantly after heat denaturing. *P < .05, compared with vehicle and untreated controls (using a 1-way analysis of variance with the (D) Dunnett post-test or (E) unpaired t tests with Welch correction). (C–E) N = 3–10 independent experiments, each with 3 or more technical replicates. AFU, arbitrary fluorescence unit; SF, serum free.