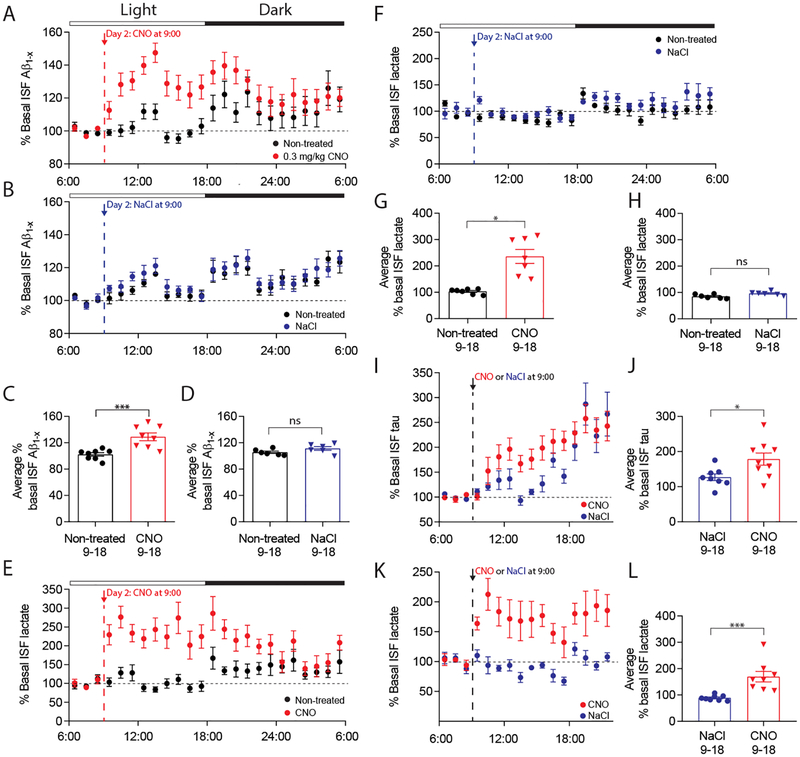
Fig. 4.
Chemogenetic activation of glutamatergic supramammillary neurons increases hippocampal ISF Aβ, tau, and lactate levels. (A) ISF Aβ levels normalized to baseline (06:00–09:00) during a 24-hour untreated period (black) and 24-hour period with CNO (red, n=8: 4F, 4M) or (B) NaCl injection (blue, n=6: 1F, 5M). (C) Average ISF Aβ was significantly increased after injection of CNO (09:00–18:00) compared to the untreated day (n=8, paired t-test). (D) NaCl control injection did not alter average ISF Aβ (n=6). (E) Normalized ISF lactate levels before and after CNO (n=7: 4F, 3M) and (F) NaCl injection (n=6). (G) Average ISF lactate was significantly increased after CNO injection (09:00–18:00) compared to the untreated day (n=7, Wilcoxon signed rank). (H) Average ISF lactate following control NaCl injection (09:00–18:00) was unchanged. (I) ISF tau levels normalized to baseline (06:00–09:00) in CNO-treated mice (n=9: 3F, 6M) and NaCl-injected controls (n=8: 4F, 4M). (J) ISF tau post CNO treatment (09:00–18:00) was significantly increased compared to NaCl controls (n=8–9, unpaired t-test). (K) Normalized ISF lactate levels of CNO (n=8: 3F, 5M) and NaCl-treated mice (n=8: 4F, 4M). (L) Average ISF lactate post CNO treatment (09:00–18:00) was increased compared to NaCl controls (n=8, Mann-Whitney). All data represent mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001.