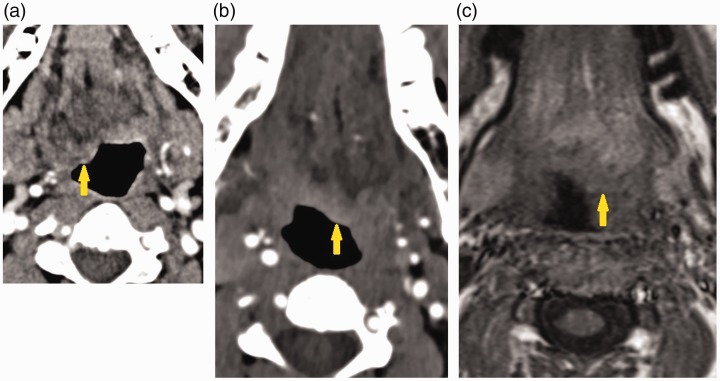
Figure 2.
(a) Neck computed tomography angiogram (CTA) in patient one shows bulbous protrusion of the right hemitongue into the oropharynx (arrow). (b) Neck CTA in patient two neck protrusion of the left hemitongue into the oropharynx consistent with tongue paralysis (arrow). (c) T1-weighted fat-suppressed magnetic resonance imaging in patient two shows protrusion of the left hemitongue into the oropharynx (arrow).