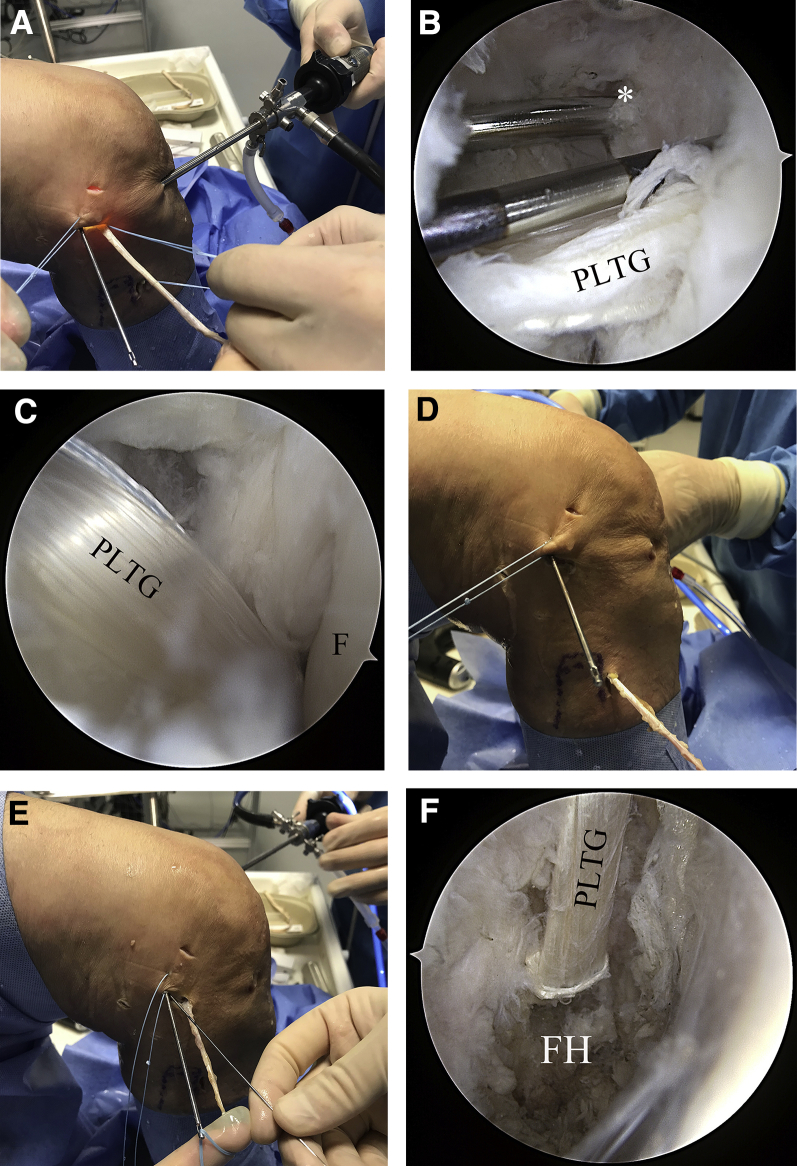
Fig 6.
We recommend using a gracilis or semitendinosus tendon graft, with a length of at least 20 cm. (A) The armed graft is shuttled into the femoral PLT tunnel and fixed with a bioabsorbable interference screw. (B) Again, a nitinol wire may be of use for retaining the tunnel position while the PLTG is fixed; the LCL (*) drill channel can be seen posterior to the PLT tunnel. (C) The PLTG is then shuttled into the posterolateral recessus, along the native PLT. At this point, precise anatomic placement of the graft is crucial. Interposition of soft tissue must be meticulously avoided. (D) The graft is further shuttled through the fibular tunnel in the posteromedial-to-anterolateral direction. (E) The graft is then shuttled to the lateral stab incision and into the femoral LCL tunnel. (F) The implanted PLTG can be observed though the posteromedial portal. (LCL, lateral collateral ligament; PLT, popliteus muscle tendon; PLTG, popliteus tendon graft.)