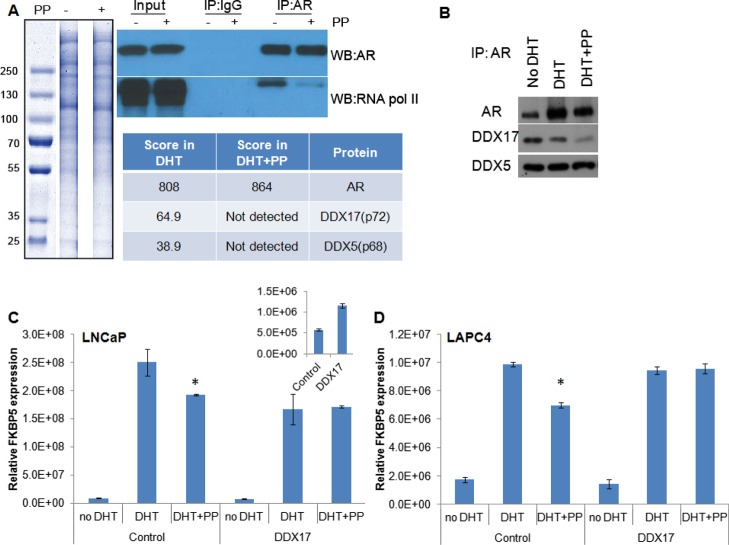
Figure 3.
IP–MS to identify AR-binding proteins affected by pyrvinium. (A) LNCaP cells were treated with 1 nM DHT ± 100 nM PP (indicated by a “–“ or “+” adjacent to “PP”. Cells were lysed, AR was immunoprecipitated and proteins resolved by SDS-PAGE. Sections from a Coomassie-stained gel were isolated and prepared for MS analysis. A western blot was also performed to demonstrate the specificity for AR pull-down and PP activity, as it is known to block the interaction with RNA pol II. The table indicates the arbitrary score from each lane for the detection of AR and DDX proteins, with approximate mass. (B) To confirm the loss of DDX protein binding, LNCaP cells were treated with vehicle, DHT, or DHT + PP for 24 h, at which point the cells were lysed and AR was immunoprecipitated. Western blot for AR and DDX17 demonstrates a loss of coprecipitation of DDX17 with AR in the presence of PP. (C) LNCaP or (D) LAPC4 cells were transfected with a DDX17 expression vector or control vector. The following day, the indicated drugs were added, and 24 h later, RNA was harvested. qPCR demonstrated a decrease in the efficacy of PP to inhibit the transcription of the AR target gene FKBP5 upon DDX17 overexpression. * significantly different compared to DHT alone (p < 0.05).