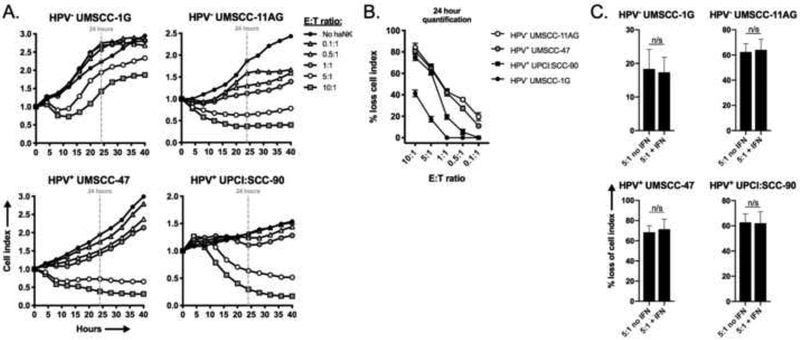
Figure 1 – haNKs variably induce cytolysis of a panel of HNSCC cell lines.
HPV-negative cell lines UM-SCC-1G (1×104 cells/well) and −11AG (1×104 cells/well) and HPV-positive cell lines UM-SCC-47 (0.75×104 cells/well) and UPCI:SCC-9 (2×104 cells/well) were plated and allowed to gain impedance overnight prior to the addition of haNKs at the indicated E:T ratios. Cell index plots normalized to the addition of haNKs at time 0. Representative impedance plots shown in (A). Percent loss of cell index relative to control (no haNKs) 24 hours after the addition of haNKs quantified in (B). Cells were pretreated with IFNγ (20 ng/mL for 24 hours) and NK cytolysis was assessed via impedance analysis at select E:T ratios. n/s, non-significant; student’s t-test.