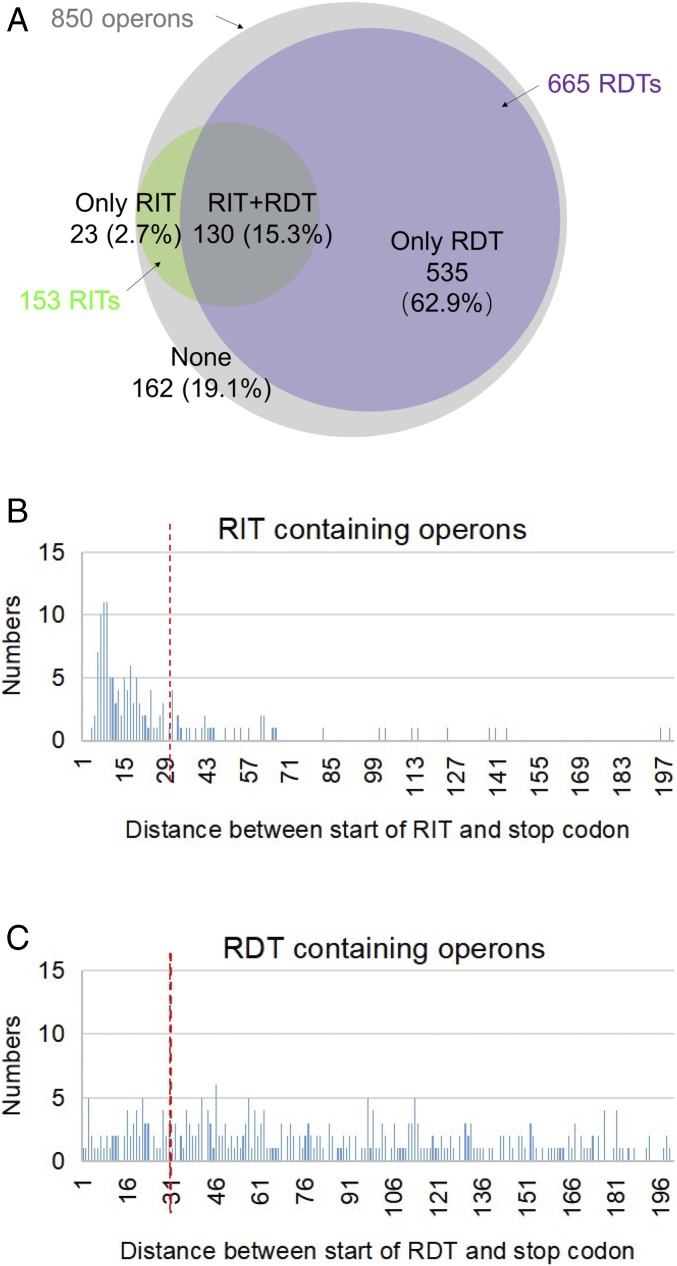
Fig. 6.
In silico analyses of RITs and RDTs at the end of 850 operons in E. coli. (A) To get an overview of the genome distributions of terminators, RIT and RDT were predicted, and distance of terminators to termination stop codons was analyzed. First, we got the operon organization information from database DOOR (42), 850 operons with more than one ORF were annotated in the genome of E. coli MG1655. Next, RITs were collected from WebGeSTer DB (41). RDTs were predicted using the EMBOSS freak program (43). The specific parameter settings are described in SI Appendix, Supplementary Materials and Methods. Finally, the RITs and RDTs located downstream of 850 operons were collected and analyzed. The Venn diagram illustrates the occurrence of RITs (green) and RDTs (violet) at the end of 850 operons (gray). (B) Bar graph demonstrating the number of operons containing RIT signal and distance (in nucleotides) between the stop codon of the last cistron of the operon and the RIT signal. The vertical red broken line indicates the distance of 30 nucleotides. (C) Bar graph demonstrating the number of operons containing RDT signal and distance (in nucleotides) between the stop codon of the last cistron of the operon and the RDT signal. The vertical red broken line indicates the distance of 30 nucleotides.