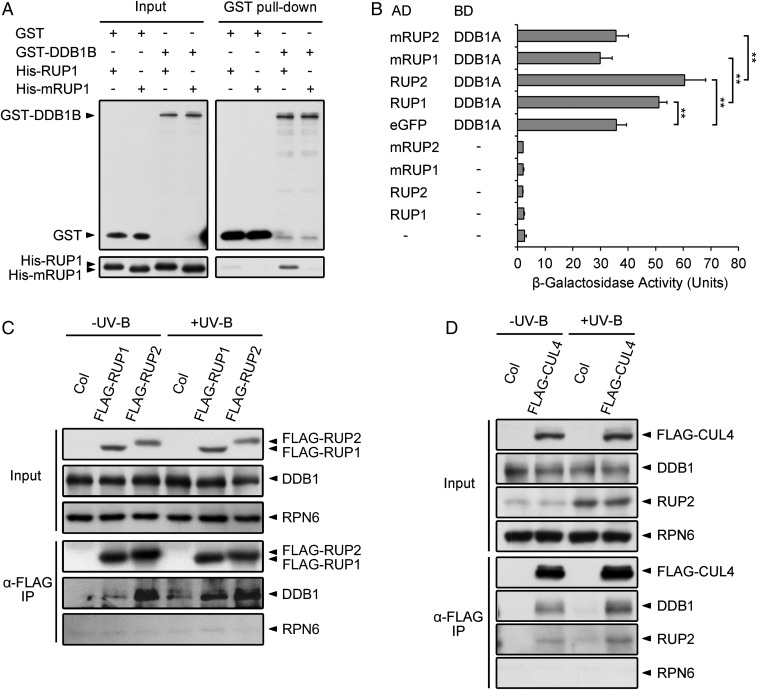
Fig. 2.
RUP1 and RUP2 interact with DDB1 via their DWD motifs. (A) RUP1 interacts with DDB1B in vitro. Purified GST or GST-DDB1B was incubated with His-RUP1 or His-mRUP1 before being pulled down by Glutathione Sepharose 4B. His-RUP1 and His-mRUP1 were detected by anti-RUP1 antibodies. (B) RUP1 and RUP2 interact with DDB1A in yeast two-hybrid assays. β-Galactosidase activity was quantified using o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside as a substrate (mean ± SD, n = 3). The asterisks indicate significant differences by Student’s t test (**P < 0.01). (C) FLAG-RUP1 and FLAG-RUP2 associate with DDB1 in Arabidopsis. Total proteins were extracted from 4-d-old seedlings grown under −UV-B and +UV-B light conditions for co-IP with ANTI-FLAG Magnetic Beads. Proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG, anti-DDB1, and anti-RPN6 antibodies. RPN6 was used as a loading and negative control. (D) FLAG-CUL4 associates with DDB1 and RUP2 in Arabidopsis. Total proteins were extracted from 4-d-old seedlings grown under −UV-B and +UV-B light conditions for co-IP with ANTI-FLAG Magnetic Beads. Proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG, anti-DDB1, anti-RUP2, and anti-RPN6 antibodies. RPN6 was used as a loading and negative control.