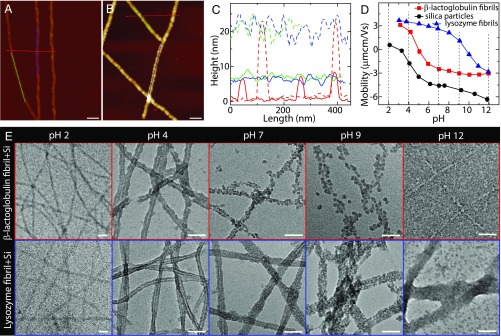
Fig. 1.
Interaction between amyloid fibril and silica. (A) AFM image of -lactoglobulin amyloid fibrils at pH 4. (B) AFM image of the mixture of -lactoglobulin fibril and silica precursor at pH 4: Silica deposited onto fibril surfaces lead to the formation of fibril–silica core–shell nanofilaments. (C) Height profiles of bare fibrils in A (solid lines) and silicified fibrils in B (dashed lines). (D) Electrophoretic mobility of -lactoglobulin fibril, lysozyme fibril, and silica as a function of pH. The isoelectric points of -lactoglobulin and lysozyme fibrils are around 5 and 10, respectively. (E) TEM images of the mixtures of fibril and silica precursor at different pHs: -lactoglobulin (Upper) and lysozyme (Lower). The concentrations of fibril and silica precursor (TEOS) are 0.1 wt % and 20 mM, respectively. (Scale bars for A, B, and E: 50 nm.)