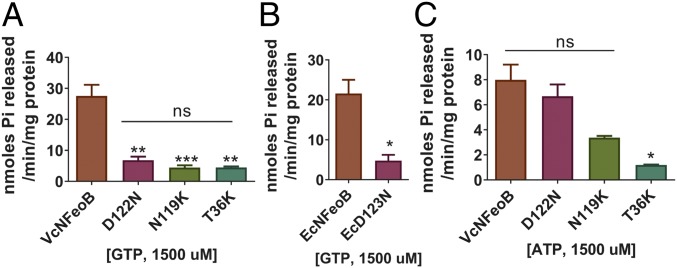
Fig. 3.
Mutants of the G4 motif (D122N and N119K) still possess ATPase activity. (A and B) GTP hydrolysis activities of the mutants were compared using 1,500 µM GTP. Mutants of VcNFeoB (A) and EcNFeoB (B) showed significantly decreased GTPase activity compared with the wild-type VcNFeoB and EcNFeoB, respectively, similar to the negative control G2/switch I mutant T36K. (C) ATP hydrolysis activities of the mutants were compared using 1,500 µM of ATP. While the T36K mutant was deficient in ATP hydrolysis, the ATPase activities of the G4 motif mutants of VcNFeoB were not significantly different from the wild type. The N119K protein required solubilization and refolding, reducing its activity compared with the other proteins. Asterisks (*, **, or ***) represent statistical significance by t test (B) or one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (A and C) at the levels of 0.05, 0.01, or 0.001, respectively.