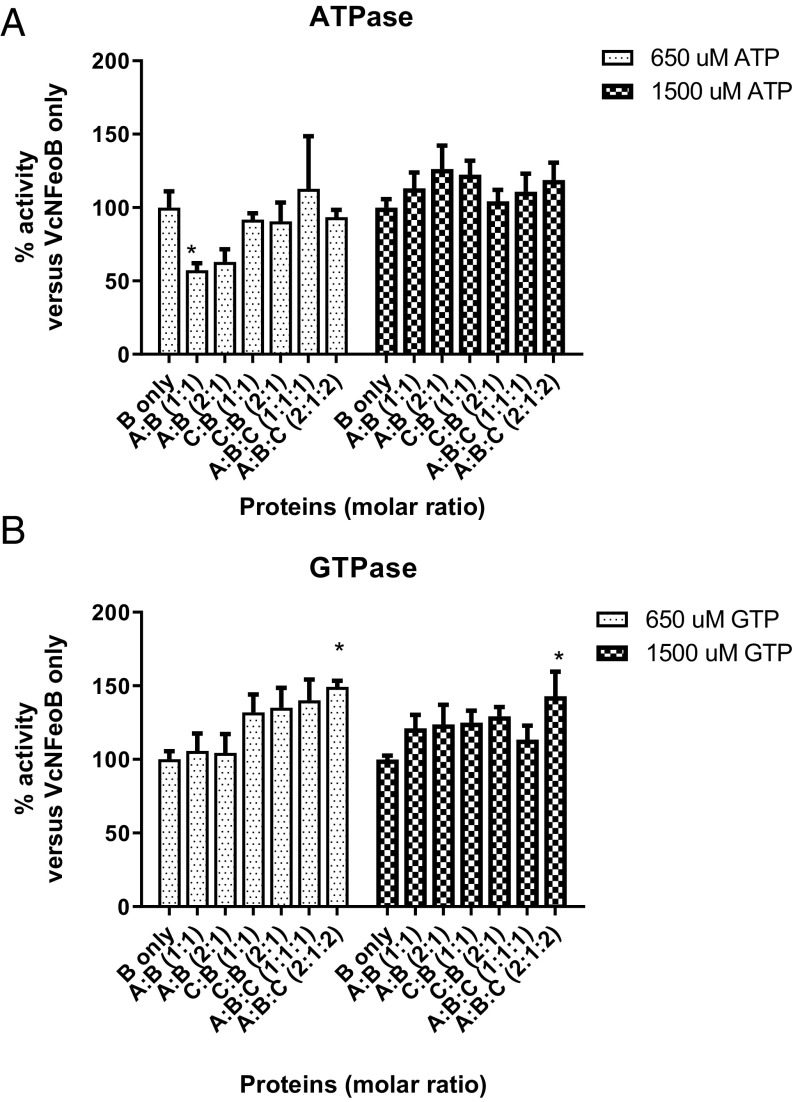
Fig. 8.
VcFeoA and VcFeoC affect nucleotide hydrolysis activity of VcNFeoB. FeoA and FeoC were mixed with VcNFeoB with molar ratios of 1:1 or 2:1 (A:B and C:B) and 1:1:1 or 2:1:2 (A:B:C). Nucleotide hydrolysis activity was compared with VcNFeoB at 650 and 1,500 µM of ATP or GTP, concentrations that are close to the KM of each nucleotide and the maximum concentrations of substrate for the malachite green assay. Percentage of activity is expressed as activity versus its activity without addition of FeoA or FeoC. (A) FeoA inhibited ATPase activity of VcNFeoB at low ATP concentration, but showed no effect at high ATP concentration or when FeoC was present as well. (B) FeoC stimulated GTPase activity of VcNFeoB at both low- and high-GTP concentrations, although only the FeoA, FeoB, and FeoC combination in a 2:1:2 molar ratio showed a statistical difference. Asterisks (*) represent statistical significance by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test at the level of 0.05.