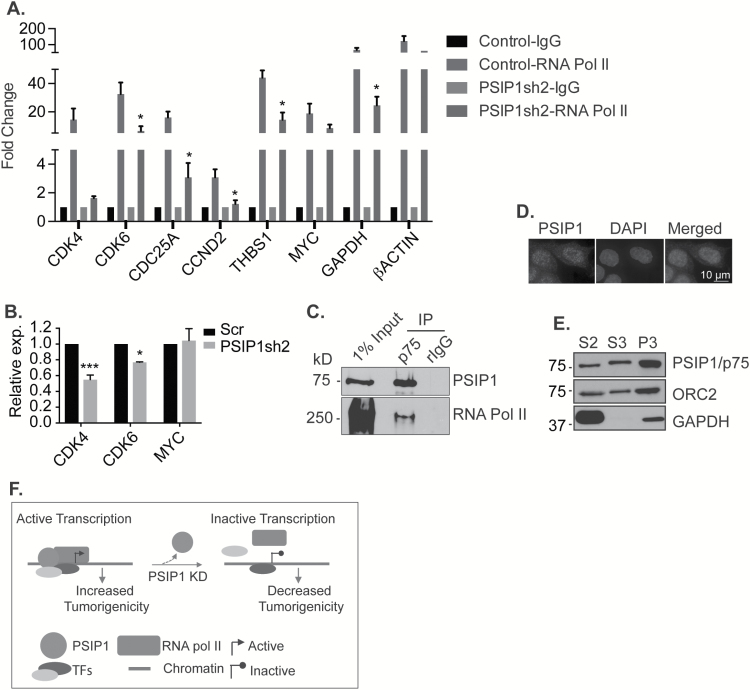
Figure 5.
PSIP1 modulates the association of RNA pol II to the promoters of cell cycle genes. (A) RNA pol II ChIP-qPCR to determine the association of RNA pol II on the promoters of genes in control and PSIP1-depleted M4 cells. β-actin is used as positive control. Graph is plotted from three independent experiments, and error bars represent SEM. (B) Nascent RNA capture assay shows the level of newly synthesised RNA from representative genes in control and PSIP1-depleted M4 cells. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001. (C) Endogenous co-IP reveals interaction between endogenous PSIP1/p75 and RNA pol II. (D) Immunofluorescence staining showing the localization of PSIP1 in M4 cells. DNA is counterstained with DAPI. Scale represents 10 μm. (E) Chromatin fractionation of M4 cells showing the enrichment of PSIP1 in MNase resistant chromatin fraction (P3). S2 and S3 represent cytoplasmic and soluble nuclear fractions respectively. Orc2 and GAPDH are used as control for MNase resistant chromatin and cytoplasmic fraction, respectively. (F) Proposed model depicting the involvement of PSIP1/p75 in regulating the association of RNA pol II on the promoters of cell cycle genes. It is possible that PSIP1 could regulate promoter association of RNA pol II through recruiting and/or stabilizing other transcription factors.