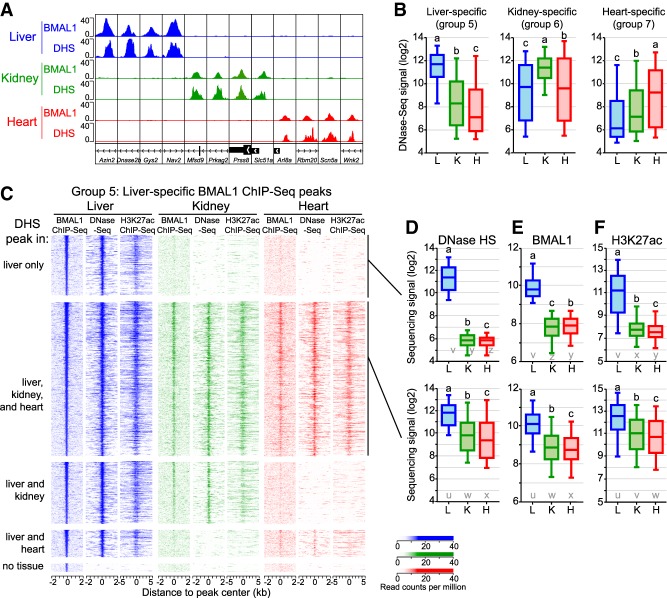
Figure 2.
The chromatin environment shapes tissue-specific BMAL1 binding. (A) Genome browser view of BMAL1 ChIP-seq and DNase-seq signals in the mouse liver, kidney, and heart at 12 BMAL1 tissue-specific peaks. (B) DNase-seq signal calculated at BMAL1 peak center ±250 bp in the mouse liver, kidney, and heart for tissue-specific BMAL1 peaks. Groups with different letters are statistically different. P < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test. (C) BMAL1 ChIP-seq, DNase-seq, and H3K27ac ChIP-seq signal at liver-specific BMAL1 peaks, parsed based on the presence of a DHS peak in the liver, kidney, and heart. BMAL1 ChIP-seq and DNase-seq signals are displayed with a window of ±2 kb, whereas H3K27ac ChIP-seq signal is displayed with a window of ±5 kb. (D–F) Quantification of DNase-seq (D), BMAL1 ChIP-seq (E), and H3K27ac ChIP-seq (F) signals for liver-specific BMAL1 peaks located at (group 5A; top) liver-specific DHS or (group 5B; bottom) DHS peaks common to the liver, kidney, and heart. Groups with different letters are statistically different. P < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test. u–z denote the outcome of the statistical analysis performed using groups 5A and 5B together.