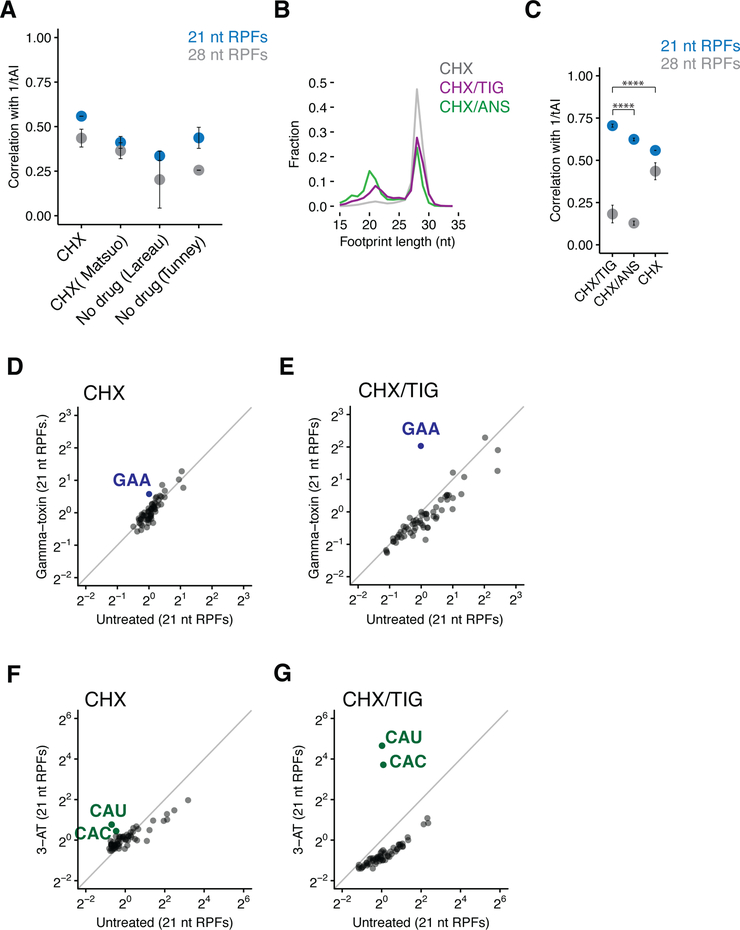
Figure 2. 21 nt RPFs correlate with the tRNA abundance metrics.
(A) Spearman rank correlations of A-site codon-specific occupancies with the inverse of tRNA adaptation index (tAI) from ribosome profiling libraries prepared with CHX (our samples or (Matsuo et al., 2017)) or no elongation inhibitor in the lysates (n≥2, ±SD). (Lareau et al., 2014; Tunney et al., 2017) (B) Length distributions of ribosome footprints comparing libraries prepared with CHX only (grey), CHX/TIG (purple), and CHX/ANS (green) in the lysates. (C) Spearman rank correlations of A-site codon-specific occupancies with 1/tAI from samples described in (B) (n≥2, ±SD). p-values for 21 nt RPFs from Student’s t-test after Fisher’s z-transformation is indicated by asterisks. ****, p< 0.0001. (D and E) Scatter plots of codon-specific ribosome occupancies for 21 nt RPFs comparing gamma-toxin treated to untreated cells from libraries prepared with CHX only (D) or CHX/TIG (E) in the lysates. GAA codons are colored in blue and labeled. (F and G) Scatter plots of codon-specific ribosome occupancies for 21 nt RPFs comparing 3-AT treated relative to untreated cells from libraries prepared with CHX only (F) or CHX/TIG (G) in the lysates. Both histidine codons are colored in green and labeled.