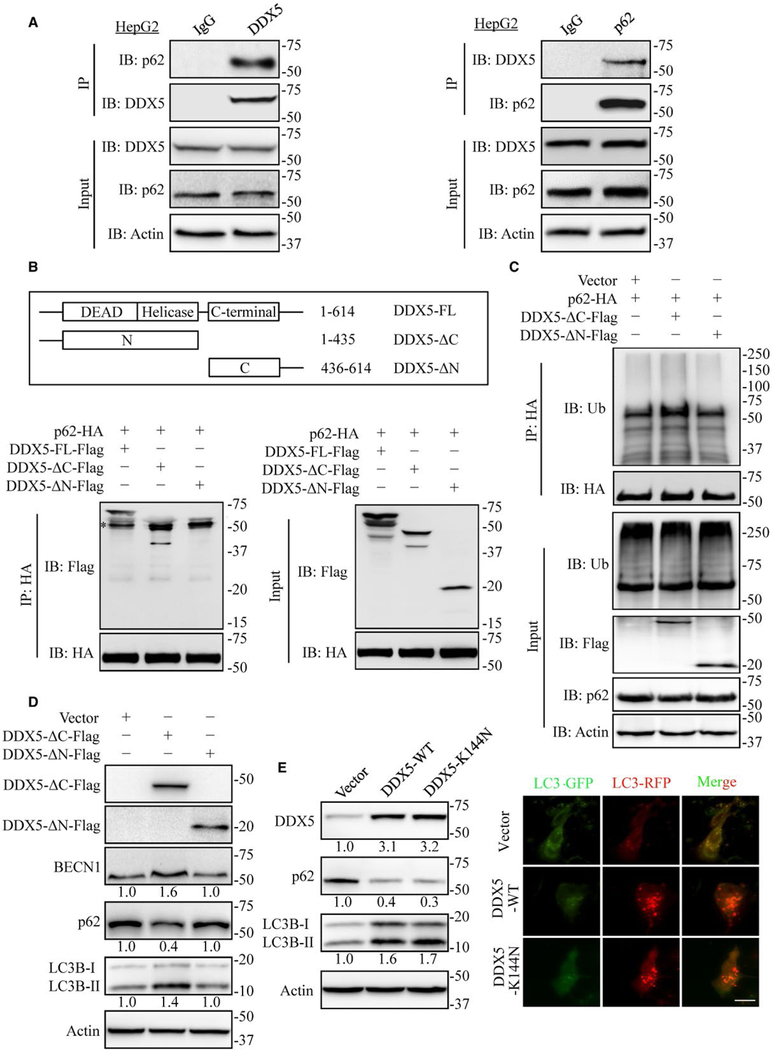
FIG. 4.
DDX5 is a p62 interacting protein. (A) HepG2 extracts were coimmunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-DDX5 antibody or IgG and followed by immunoblot (IB) analyses with anti-p62 antibody (left) and IP with anti-p62 antibody or IgG followed by blotting with anti-DDX5 antibody (right). Data are representative immunoblots of three independent assays. (B) Mapping of DDX5 regions involved in p62 binding. Top: deletion mutants of DDX5. Bottom: HEK293T cells were co-transfected with p62-HA and indicated constructs of DDX5-Flag. Cell extracts were IP with anti-HA antibody. Data are representative immunoblots of three independent assays. *, heavy chain. (C) HEK 293T cells were co-transfected with p62-HA and indicated constructs of DDX5-Flag expression plasmids for 48 hours and then treated with MG132 (10 μmol/L) for 4 hours. The cell lysates were extracted and immunoprecipitated using anti-HA antibody. Ub, ubiquitin. (D) The N-terminal domain of DDX5 affected the expression of autophagy-related proteins detected by immunoblotting. Data are representative immunoblots of three independent assays. (E) DDX5 promotes autophagy independent of its RNA binding and helicase activity. HepG2 cells were transfected with DDX5-WT and DDX5-K144N, indicated proteins were detected by immunoblotting (left), and the flux rate of autophagy was measured (right). Scale bar = 10 μm.