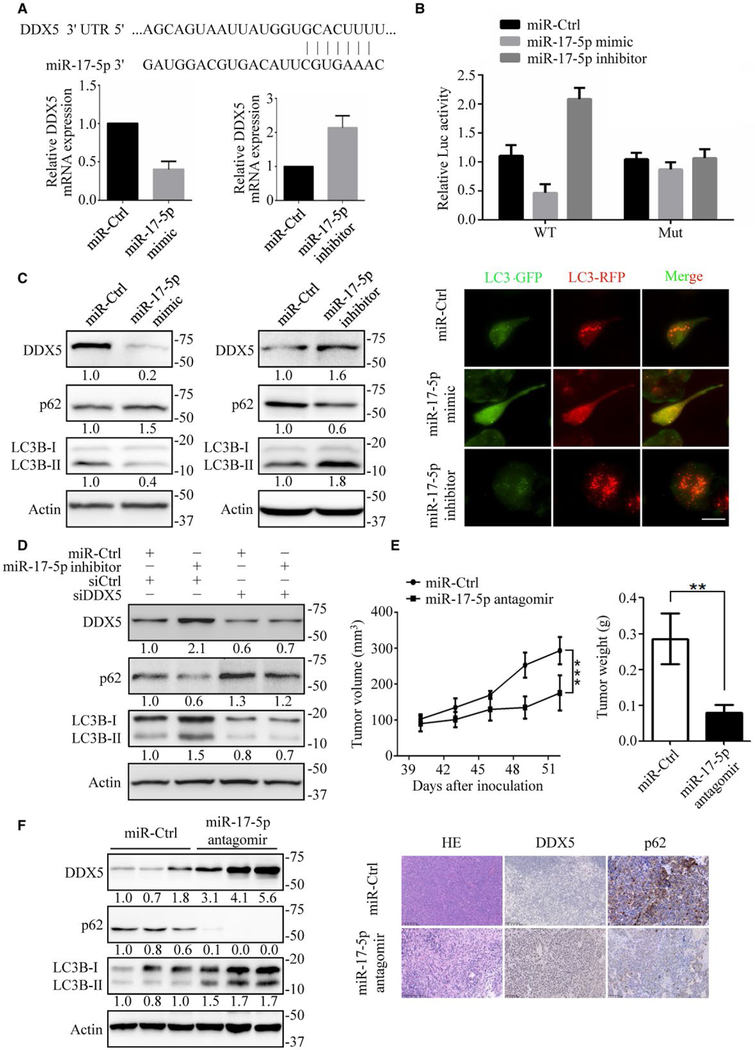
FIG. 7.
MiR-17–5p downregulates DDX5 to promote tumorigenesis. (A) Top: Diagram showing the putative miR-17–5p-targeting seed sequence on DDX5–3′ UTR. Bottom: Relative DDX5 mRNA expression upon transfection with miR-17–5p mimic or miR-17–5p inhibitor in HepG2 cells. (B) Fold change in luciferase activity driven by the WT (wide-type) or Mut (mutant) DDX5–3′ UTR reporter under miR17–5p mimic or miR-17–5p inhibitor treatment in HepG2 cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (C) Immunoblots of autophagy-related proteins in HepG2 cells transfected with miR17–5p mimic and miR-17–5p inhibitor (left), and the flux rate of autophagy was detected by infecting adenovirus with mRFP-GFP-LC3 (right). Scale bars = 10 μm. (D) Knockdown of DDX5 reversed miR-17–5p inhibitor mediated autophagy promotion. Autophagy-related proteins were detected by immunoblotting. (E) HepG2 cells were inoculated in the flanks of nude mice. Upon the tumor xenografts reaching 100 mm3, miR-Ctrl or miR-17–5p antagomir were continuously intratumorally injected for 2 weeks. Left: tumor volumes were measured every 3 days. Right: tumor weight was measured when mice were sacrificed. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 6 per group). (F) The expression of DDX5, p62 and LC3B-II/I in xenograft tumor tissues were detected by immunoblotting (left) and immunohistochemistry (right). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. NS: nonsignificant.