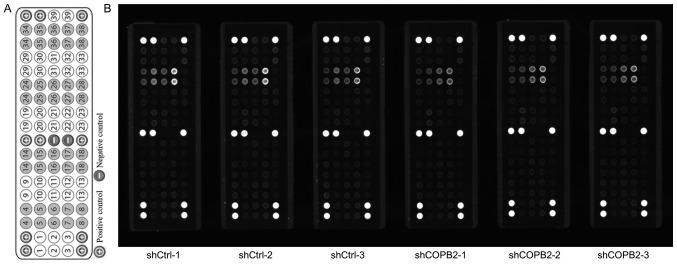
Figure 9.
Effects of COPB2 gene knockdown on specific RTK signaling pathway genes in BGC-823 cells. (A) Target map of the PathScan® RTK Signaling Antibody Array kit (Fluorescent Readout). This map image was taken from the Cell Signaling Technology website (https://www.cst-c.com.cn/product/product-Detail.jsp?productId=7949). Each site represents a target, which was indicated numerically and corresponds to the numbers presented in Table I. (B) Effects of COPB2 gene knockdown on relevant genes from the RTK signaling pathway in BGC-823 cells. This slide-based antibody array image indicated the reaction results for Lv-shCOPB2-infected and Lv-shCtrl-infected BGC-823 cells. The results demonstrated that knockdown of COPB2 significantly reduced the phos-phorylation of 23 RTK signaling pathway targets, including epidermal growth factor receptor/ErbB1, HER2/ErbB2, HER3/ErbB3, fibroblast growth factor 4, insulin receptor, tropomyosin-related kinase A/NTRK1, TrkB/NTRK2, recepteur d'origine nantais/macrophage stimulating 1 receptor, Ret, c-Kit/stem cell growth factor receptor, FMS-like receptor tyrosine kinase 3/Flk2, EphA3, EphB1, EphB4, TYRO3 protein tyrosine kinase/Dtk, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2/kinase insert domain receptor, Akt/PKB/Rac (Thr308), Akt/PKB/Rac (Ser473), ribosomal S6 kinase, c-Abl, Src, Lck and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 at different levels (P<0.05 or P<0.01). COPB2, coatomer protein complex subunit β2; Eph, EPH receptor; HER, human epidermal growth factor receptor; Lv, lentivirus; NTRK, neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase 1; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; sh, short hairpin RNA.