Figure 5.
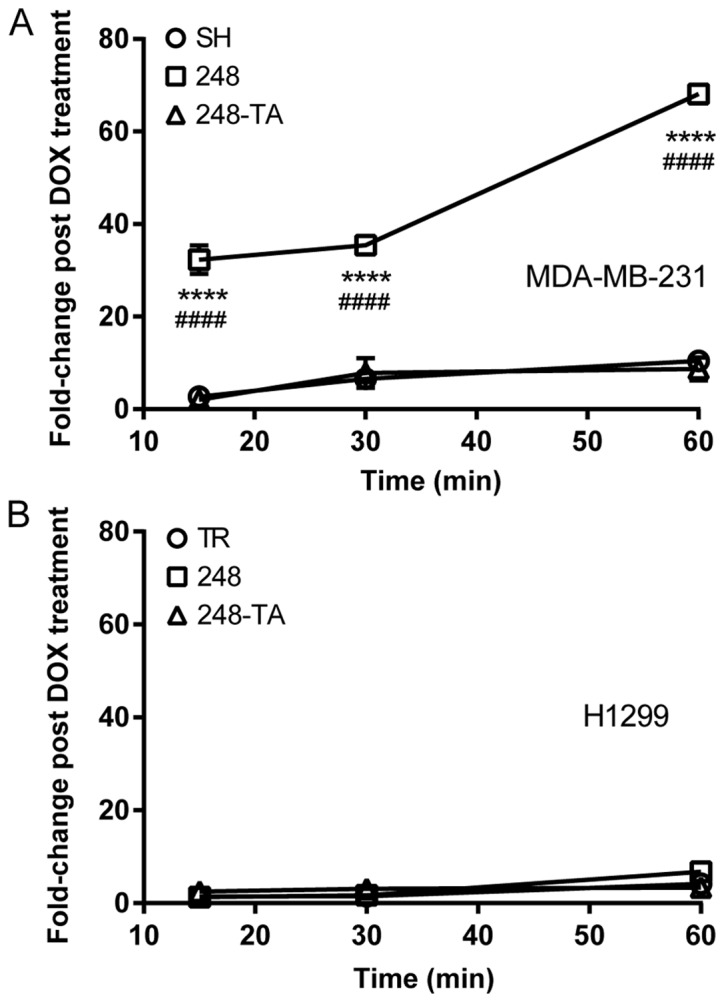
Mutant p53-R248Q results in pro-adhesive properties in a cell type- and transactivation-dependent manner. The adhesion of (A) MDA-MB-231 and (B) H1299 cells conditionally expressing indicated p53 variants to a tissue culture plate was measured. The cells were seeded and then rinsed off the plate at the indicated time-points. The remaining cells were counted and the number of adhered DOX-treated cells relative to the number of adhered non-treated cells (fold-change post DOX treatment) was plotted. The data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. ****P<0.0001 vs. control group, two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test; ####P<0.0001 R248Q vs. R248Q-TA group, two-way ANOVA with Sidak post-hoc test. p53, tumor suppressor p53; DOX, doxycycline; ANOVA, analysis of variance; TR, cells with Tet repressor only; SH, cells with silenced endogenous p53; TA, transactivatory domain disruption (L22S/W23Q) in addition to R248Q mutation.
