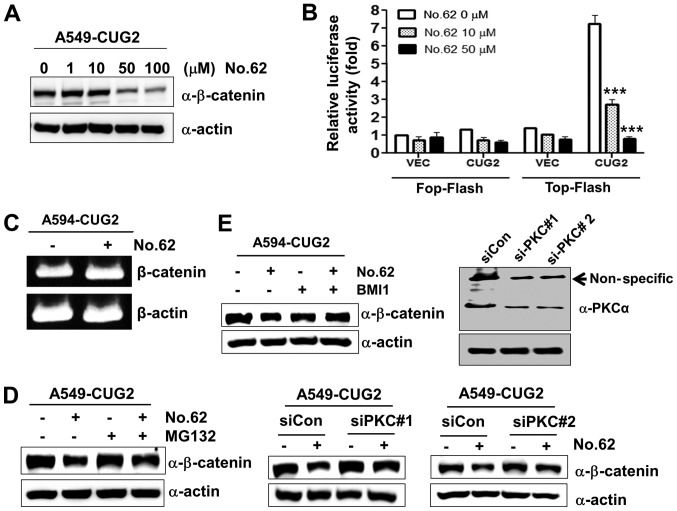
Figure 4.
CGK062 treatment destabilizes β-catenin in a proteasome- and PKCα- dependent manner. (A) A549-CUG2 cells were treated with CGK062 (0, 1, 10, 50 and 100 µM) for 24 h, and β-catenin levels were measured by performing western blot analysis with an anti-β-catenin antibody. (B) A549-CUG2 cells were transfected with the Top-Flash (1 µg) or Fop-Flash (1 µg) luciferase reporter vector in the presence of CGK062 (50 µM) and were harvested at 48 h following transfection. Transfection efficiency was normalized with that of the β-galactosidase reporter vector pGK-βgal (1 µg) during the measurement of luciferase activity. Results shown are an average of 3 experiments; bars indicate the means ± SD (***P<0.001, 0 vs. 10 µM, 0 vs. 50 µM). (C) Total RNAs (3 µg) were isolated from A549-CUG2 cells treated with or without CGK062 (50 µM), and cDNAs were synthesized using reverse transcriptase II. β-catenin gene sequences were amplified using specific primers by using an optimized PCR cycle and were visualized on 1.5% agarose gels following ethidium bromide staining. β-actin was used as an internal control. (D) A549-CUG2 cells were treated with MG132 (1 µM) for 8 h in the absence or presence of CGK062 (50 µM) and were harvested. β-catenin levels were measured by performing western blot analysis with an anti-β-catenin antibody. (E) A549-CUG2 cells were treated with BMI (7.5 µM), a specific PKCα inhibitor, or were transfected with a control and PKCα siRNAs (#1 or #2) in the absence or presence of CGK062 (50 µM) for 24 h. Transfection efficiency of PKCα siRNAs (#1 or #2) was confirmed by western blot analysis. β-catenin levels were measured by performing western blot analysis with an anti-β-catenin antibody. CUG2, cancer-upregulated gene 2; PKC, protein kinase C.