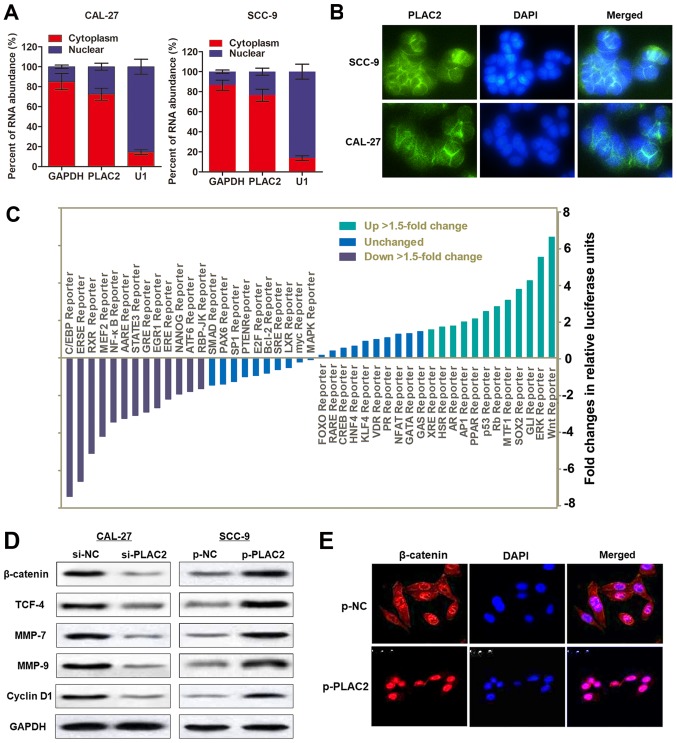
Figure 4.
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is activated by PLAC2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. (A) Nuclear fraction experiment and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction detected the abundance of PLAC2 in the nucleus and cytoplasm. GAPDH was the positive control for cytoplasm, and U1 were the positive controls for the nucleus. (B) The subcellular distribution of PLAC2 was visualized by RNA Fluorescent in situ hybridization in SCC-9 and CAL-27 cells. (C) The activity changes of indicated signaling pathways in SCC-9 cells were depicted upon overexpression of PLAC2, as indicated with a reporter activity. (D) The effect of PLAC2 on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in SCC-9 cells was assessed with a western blot analysis assay. (E) PLAC2 induced nuclear translocation of β-catenin. Immunofluorescence staining of β-catenin in SCC-9 cells treated with p-PLAC2. PLAC2, placenta-specific protein 2; MMP-7, matrix metallopeptidase-7; TCF4, transcription factor 4; p-PLAC2, PLAC2 overexpression plasmids.