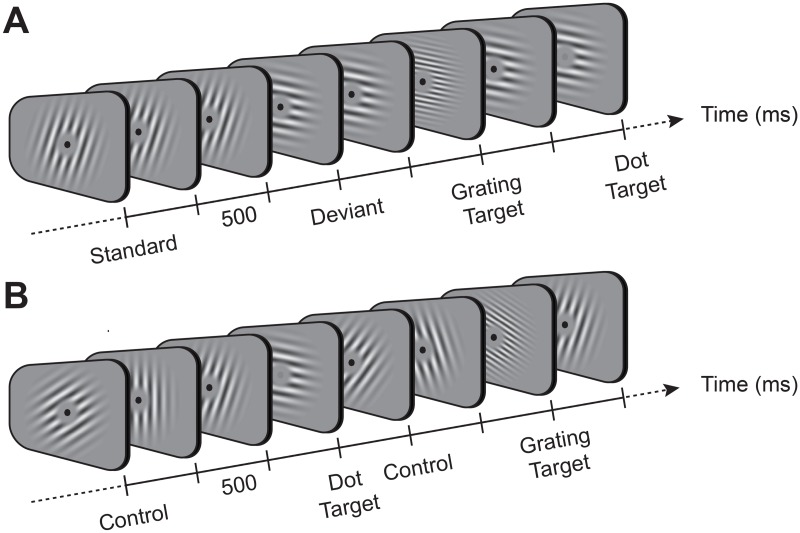
Fig 1. Example stimuli in each of the two block types used in the study.
(A) Roving oddball sequence. In this sequence, the orientation of gratings was repeated over short sequences of stimuli (‘standards’), before changing to a different orientation (‘deviant’). During the grating or dot task, participants responded to rare gratings with high spatial frequency (‘grating target’) or to rare decreases in fixation-dot contrast (‘dot target’), respectively. (B) Equiprobable sequence. In this sequence, the orientation of control gratings changed with each successive presentation.