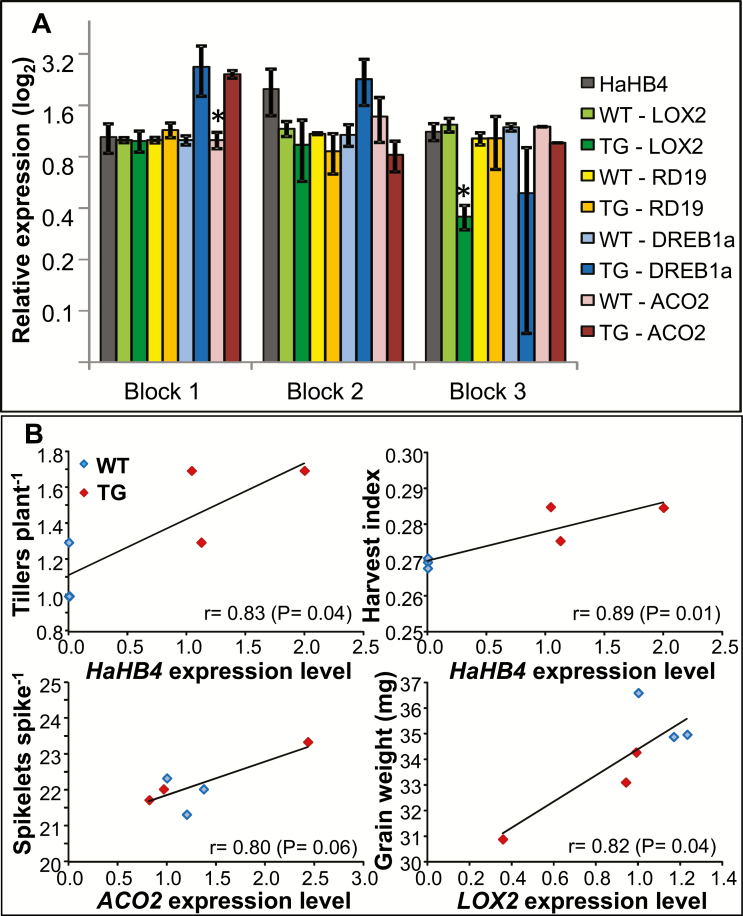
Fig. 6.
Transcript levels of HaHB4 and genes related to biotic and abiotic stresses in leaf samples collected in field trials. (A) Relative transcript levels of HaHB4, RD19, DREB1Ba, and ACO2 in leaves of 128-day-old plants (i.e. heading of the crops) of wild type Cadenza (WT) and transgenic (TG) IND-ØØ412-7, growing in one experiment (Group 4 in Supplementary Table S3) in different blocks (1, 2, 3). HaHB4 was related to the lower level, arbitrarily set to a value of 1. All the values were previously related to ACTIN level, used as the housekeeping gene. Error bars represent the SEM of three independent biological replicates, each including three technical replicates obtained from a pool of eight plants per plot. Statistical significance was computed by Student’s t-test (*P<0.05). (B) Response of ecophysiological traits to the expression level of evaluated genes. Only significant relationships (P≤0.06; n=6) are shown.