Figure 3. Protein thermal shift assay screen and characterization of RLS-24 (adapalene) as a Siah small molecule inhibitor.
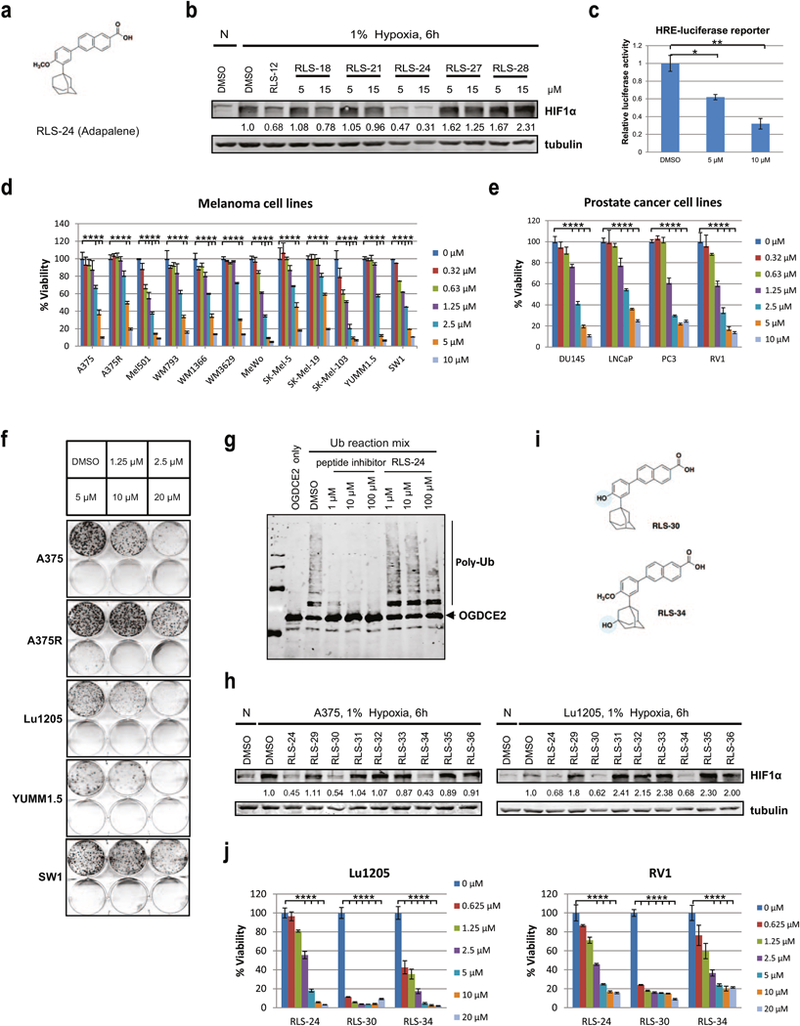
(a) Structure of RLS-24/adapalene. (b) Different compounds at 5 µM or 15 µM concentrations were added to A375 melanoma cells, which were cultured in 1% oxygen for 6 h. HIF1α levels were examined by Western Blot analysis. Quantification of immunoblots was performed using BioRad densitometer, relative to loading controls, noted under the blots. (c) A375 cells were transfected with HRE-firefly and renilla luciferase plasmids for 24 hours and treated with 2 µM or 10 µM of adapalene (RLS-24) under hypoxia. After 24 hours, cells were lysed and subjected to a luciferase assay. Data were calculated relative to DMSO-treated cells. Means ± standard errors calculated from three experiments. *p <0.05, **p < 0.01, compared to controls (one-way ANOVA). (d) Different human and mouse melanoma cells were treated with indicated concentrations of RLS-24, and cell viability was assessed by ATPlite after 72 h. Each bar represents the mean ± standard deviation of three measurements. Representative data was shown. ****p < 0.0001 was calculated based on comparison with the control (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test). (e) Different human prostate cancer cells were treated with indicated concentrations of RLS-24, and cell viability was assessed by ATPlite after 72 h. ****p < 0.0001, compared to control (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test). (f) Indicated human and mouse melanoma cells were plated at low density and grown in medium containing different concentrations of RLS-24. The number of colonies formed after 10 days in culture was determined by crystal violet staining. (g) Indicated concentrations of RLS-24 and a Siah peptide inhibitor (as a positive control) were incubated with purified Siah2 for 30 min, followed by addition of Siah2 substrate OGDCE2 and ubiquitination reagents (E1, E2, Ub). Mixtures were then incubated at 37°C for 45 min and subjected to Western Blot an alysis. (h) A375 and Lu1205 melanoma cells were treated with RLS-24 and derivatives for 6 h under hypoxia. Whole cell lysates were immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. Quantification of immunoblots was performed using BioRad densitometer, relative to loading controls, noted under the blots (i) Structures of RLS-24 derivatives RLS-30 and RLS-34. (j) Cells of the melanoma line Lu1205 and the prostate cancer line RV1 were treated with different concentrations of RLS-24, RLS-30 or RLS-34. Cell viability was assessed by ATPlite after 72 h. ****p < 0.0001 was calculated based on comparison with the control (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test).
