Figure 5.
Altered Mitotic Kinetics, Mitochondrial Morphology, Cell Survival, and Tumorigenicity of ESI-CNV hPSCs and BCL-XL Overexpression Cells
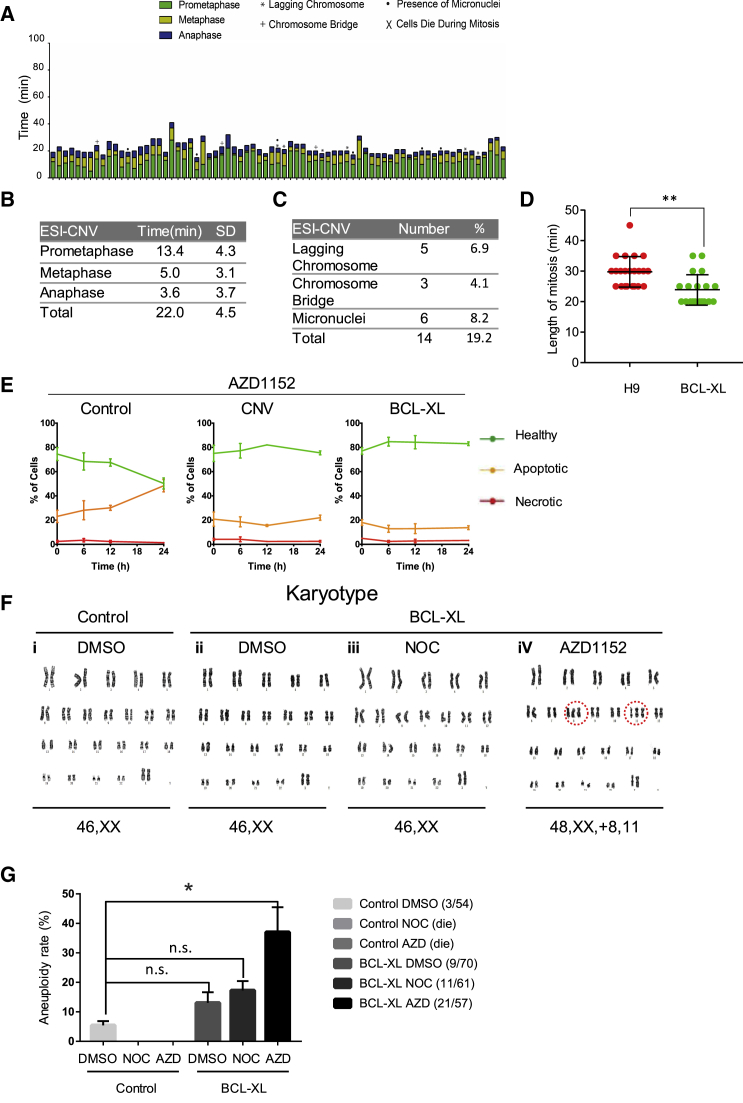
(A) Quantitative analysis of the length of each phase of the mitosis of ESI-CNV cells (n = 73, data pooled from more than three independent experiments) based on time-lapse movies. Prometaphase, metaphase, and anaphase are represented by different colors, and different types of division defects are marked by indicated symbols as in Figure 1.
(B) Mean duration (minutes) of prometaphase, metaphase, and anaphase of ESI-CNV-H2B-mCherry cells.
(C) Frequency of defective divisions in ESI-CNV-H2B-mCherry cells.
(D) Dot plot of the mitosis duration in wild-type H9 (n = 23) and BCL-XL OE (n = 21) cells. Each dot represents one cell measured in the time-lapse video (data pooled from three independent experiments). Data are presented as mean ± SEM; ∗∗p < 0.01, based on unpaired Student's t test.
(E) ESI-035 control, CNV, and BCL-XL OE cell lines were cultured for 24 h in the presence of 100 nM AZD. The levels of apoptosis were measured at 6, 12, and 24 h following inhibitor exposure. Solid lines indicate healthy cells (green), apoptotic cells (orange), and necrotic cells (red). Control cells displayed increased cell death following 24-h exposure when compared with CNV and BCL-XL OE cells. Error bars represent SEM from three biological replicates.
(F) Karyotype analysis of DMSO-, NOC-, and AZD-treated BCL-XL OE cells. Red circle highlights trisomy of chromosomes 8 and 11.
(G) Bar graph of aneuploid cell percentage in DMSO-, NOC-, and AZD-treated BCL-XL OE cells (values shown are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments; n.s., not significant; ∗p < 0.05, based on unpaired Student's t test).