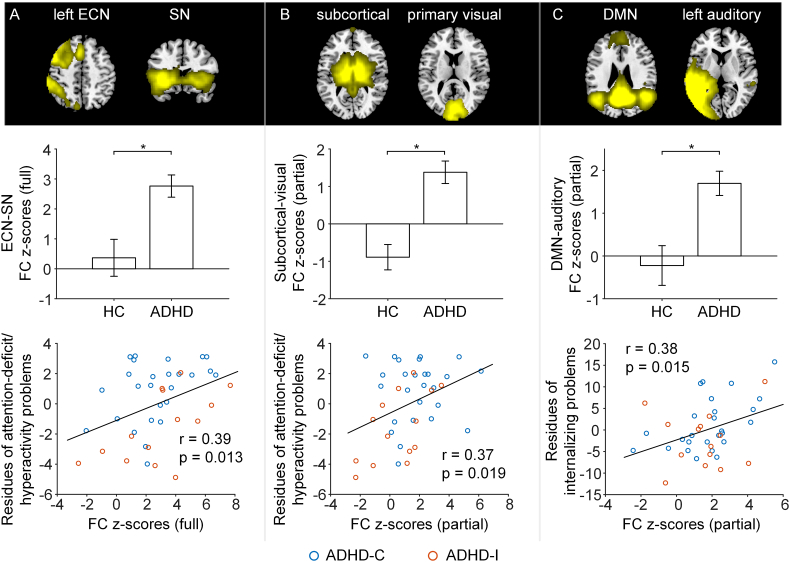
Fig. 2.
Loss of between-network functional segregation in ADHD and its association with symptom severity. Row 1: Brain slices showing the spatial maps of the two network components. Row 2: Compared to controls, ADHD had higher functional connectivity between the left ECN and the salience network (full correlation, panel A), between subcortical and visual networks (partial correlation, panel B) and between the posterior DMN and left auditory network (partial correlation, panel C). The bars and error bars indicate mean and standard error respectively. * represents p < .05 FWE corrected for all the pairs between all the ICs of interest. Row 3: The loss of between network functional segregation related to symptom severity in ADHD participants including CBCL attention-deficit/hyperactivity problems (A & B) and CBCL internalizing problems (C) (red: ADHD inattentive subtype (ADHD-I); blue: ADHD combined subtype (ADHD-C)). Abbreviations: ECN: executive control network; SN: salience network; DMN: default mode network.