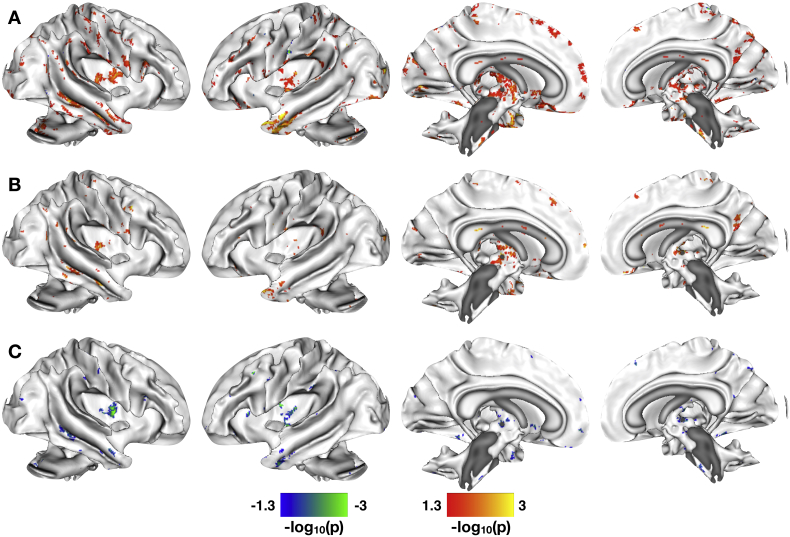
Fig. 3.
Correlations between paracellular permeability and white matter microstructural integrity. A. Significant between-group differences in the correlation of paracellular permeability and fractional anisotropy (FA). B. Significant whole-brain correlations between levels of 51Cr-EDTA passage and WM microstructure as quantified by FA for the HCs. C. Significant whole-brain correlations between levels of 51Cr-EDTA passage and WM microstructure as quantified by FA for the IBS patients. All statistical maps are thresholded at p < 0.05, Family Wise Error corrected for comparing across the whole brain. Color bars are scaled in terms of –log10(p). For the statistical maps shown in A, warm colors indicate WM tracts with significant positive between-group differences for the (IBS-HCs) contrast; cool colors indicate WM tracts with significant negative between-group differences for the (IBS-HCs) contrast. For the statistical maps shown in B–C, results are masked with significant group-differences shown in A. Warm colors indicate WM tracts with increased FA with increased paracellular passage of 51Cr-EDTA; cool colors indicate tracts with increased FA with decreased paracellular passage of 51Cr-EDTA.