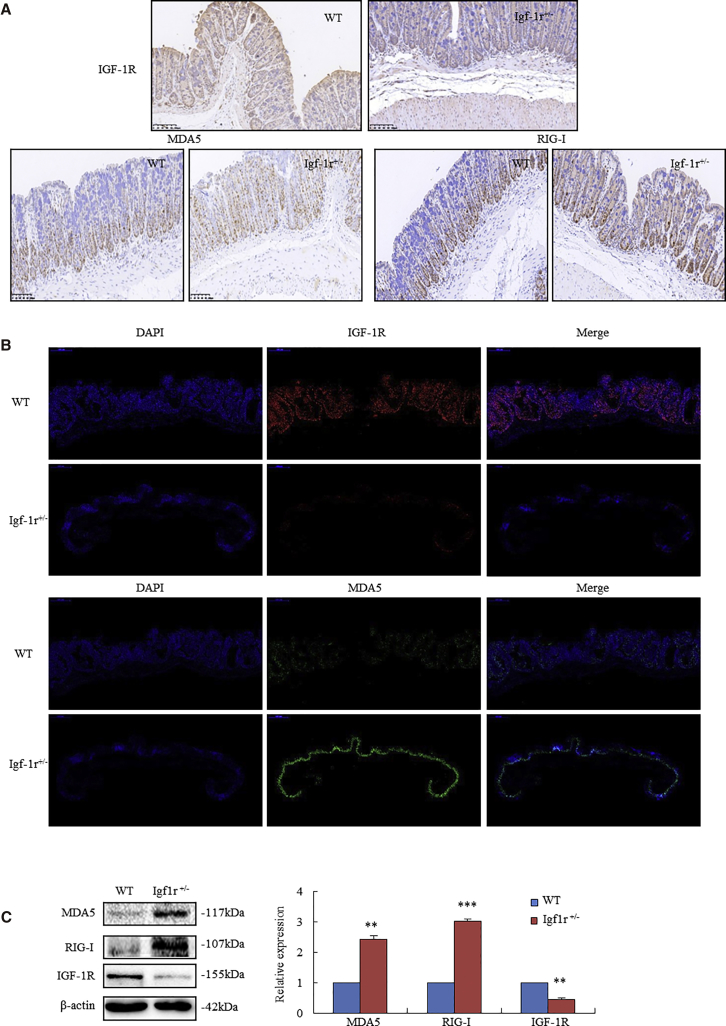
Figure 1.
Knockdown IGF-1R Triggered MDA5 and RIG-I in Igf1r+/− Mice
(A) IHC analyzed the expressions of IGF-1R, MDA5, and RIG-I in Igf1r+/− mice and their WT littermates. Blue staining identified the nuclei of colonic epithelium by DAPI. WT mice exhibited a stronger diffuse staining of IGF-1R (brown) than Igf1r+/− mice. Igf1r+/− mice had a significant increase in MDA5 (brown) and RIG-I (brown) diffused membranous and cytoplasmic staining, whereas WT mice had only scattered positivity in the basal cells of colonic crypt. (B) Immunofluorescent staining of IGF-1R and MDA5 in colorectal tissues of WT and Igf1r+/− mice. First frame: DAPI stained the nuclei of colorectal epithelium (first column). Red fluorescent staining showed IGF-1R expression in colorectal epithelium. In contrast to WT mice (first row), Igf1r+/− mice demonstrated a decreased IGF-1R expression (second row). Second frame: Igf1r+/− mice showed higher MDA5 (second row, green fluorescent staining) than WT mice (first row, very weakly green fluorescent staining). (C) Western blotting analysis showed a lower level of IGF-1R and higher levels of MDA5 and RIG-I in the colorectal epithelium of Igf1r+/− mice than WT mice. (n = 6). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 between Igf1r+/− mice and their WT littermates.