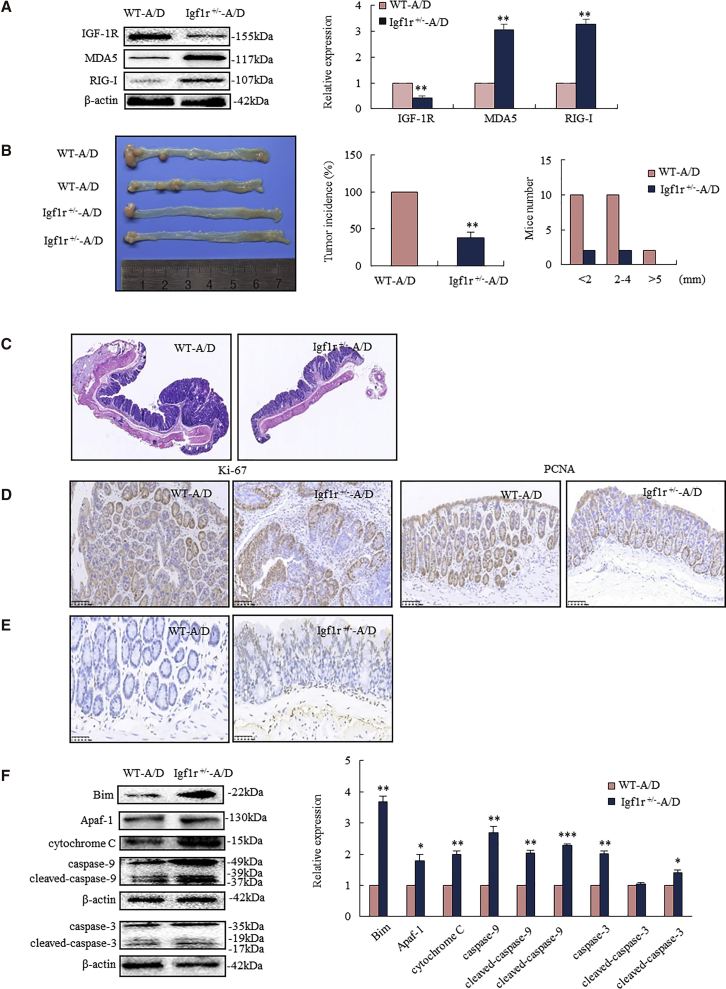
Figure 6.
IGF-1R Knockdown-Triggered MDA5 and RIG-I Mediated Mitochondrial Apoptosis, Leading to Cancer Inhibition in Igf1r+/− Mice
Igf1r+/− mice and their WT littermates were exposed to AOM-DSS for inducing colorectal cancer. (A) Igf1r+/− mice had higher MDA5 and RIG-I levels in the colorectal epithelium than WT mice. (B) Igf1r+/− mice developed less colorectal tumor than WT mice (left), showing decreased incidence (middle) and size of tumor (right). (C) Histopathological analyses showed advanced adenocarcinoma in WT mice, while only low-grade dysplastic mucosa appeared in Igf1r+/− mice. (D) IHC analysis showed a strong diffuse staining of Ki-67 and PCNA in the colorectal cancer of WT mice, whereas it showed only scattered positivity in the basal cells of colorectal crypt in Igf1r+/− mice. (E) TUNEL staining analysis showed increased apoptotic epithelium in Igf1r+/− mice. (F) Western blotting analysis showed increased Bim and apoptosome (cytochrome c, apoptotic peptidase-activating factor 1 [Apaf-1], and caspase-9 and caspase-3) in colorectal epithelium of Igf1r+/− mice (n = 6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 between Igf1r+/−-A/D and WT-A/D. A/D, AOM-DSS.