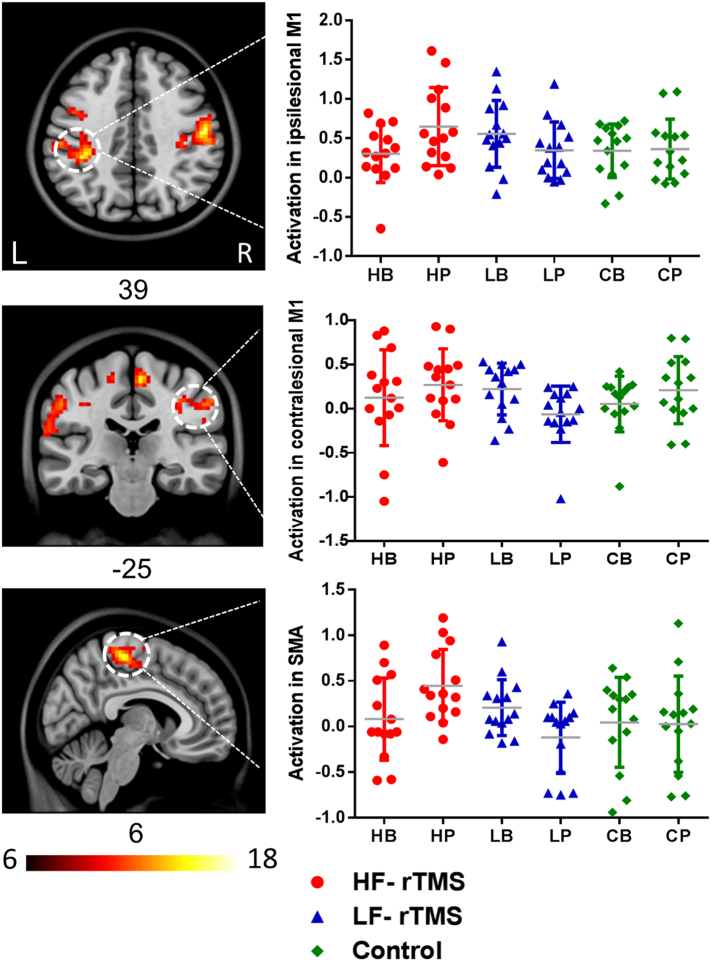
Fig. 4.
Changes in neural activity during movements of the affected hand from baseline to post-intervention were significant in bilateral M1 and SMA for high frequency (HF) rTMS, low frequency (LF) rTMS and control group (ANOVA “group × time” interaction: p < 0.01). fMRI activation of the ipsilesional M1 and SMA significantly increased in the HF-rTMS group, compared with the LF-rTMS and control groups. There was a decrease in fMRI activation of the contralesional M1 in the LF-rTMS group, compared with the HF-rTMS and control groups. rTMS, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; HB, HF-rTMS group at baseline; HP, HF-rTMS group at post-intervention; LB, LF-rTMS group at baseline; LP, LF-rTMS at post-intervention; CB, control group at baseline; CP, control group at post-intervention.