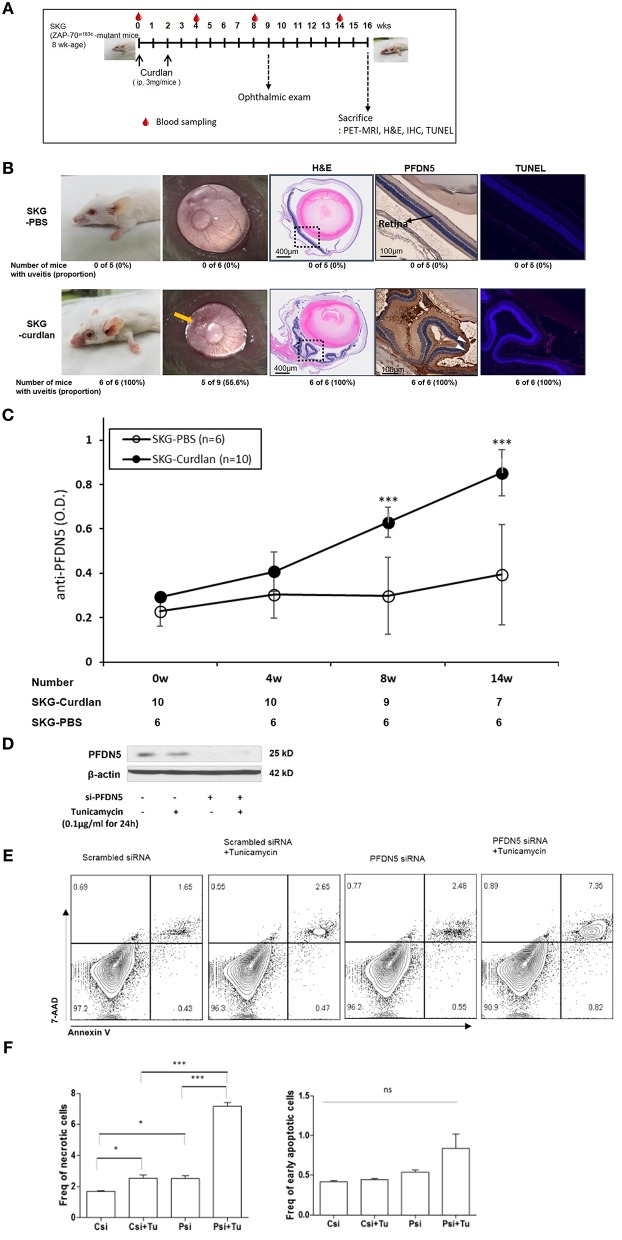
Figure 2.
Expression of PFDN5 in curdlan-treated SKG mice with ocular lesions, and the role of PFDN5 against apoptosis in ARPE19 cells. (A) The experimental design. (B) Comparison of gross phenotype, microscopic ophthalmologic exam, H&E staining, IHC, and TUNEL assay between PBS-treated SKG mice and curdlan-treated-SKG mice. (C) ELISA analysis of anti-PFDN5 antibody levels in sera of PBS-treated SKG mice and curdlan-treated SKG mice according to the number of weeks post-injection. (D) Western blot showing protein expression of PFDN5 in ARPE19 cells transfected with non-targeting scrambled siRNA, scrambled siRNA with tunicamycin stimulation, siRNA against PFDN5, and si-PFDN5 with tunicamycin stimulation. (E) Representative flow cytometry plot of 7-AAD and annexin V staining for ARPE19 cells transfected with non-targeting scrambled siRNA, scrambled siRNA with tunicamycin stimulation, siRNA against PFDN5, and si-PFDN5 with tunicamycin stimulation. (F) Comparison of the proportion of necrotic cells or early apoptotic cells among ARPE19 cells transfected with scrambled siRNA, scrambled siRNA under tunicamycin stimulation, si-PFDN5 and si-PFDN5 under tunicamycin stimulation. Data presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001, by Mann–Whitney U-test. H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; PFDN5, prefoldin subunit 5; IHC, immunohistochemistry; TUNEL, Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP Nick-End Labeling; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ARPE19, retinal pigment epithelial 19; 7-AAD, 7-aminoactinomycin D; ns, not significant.