Fig. 3.
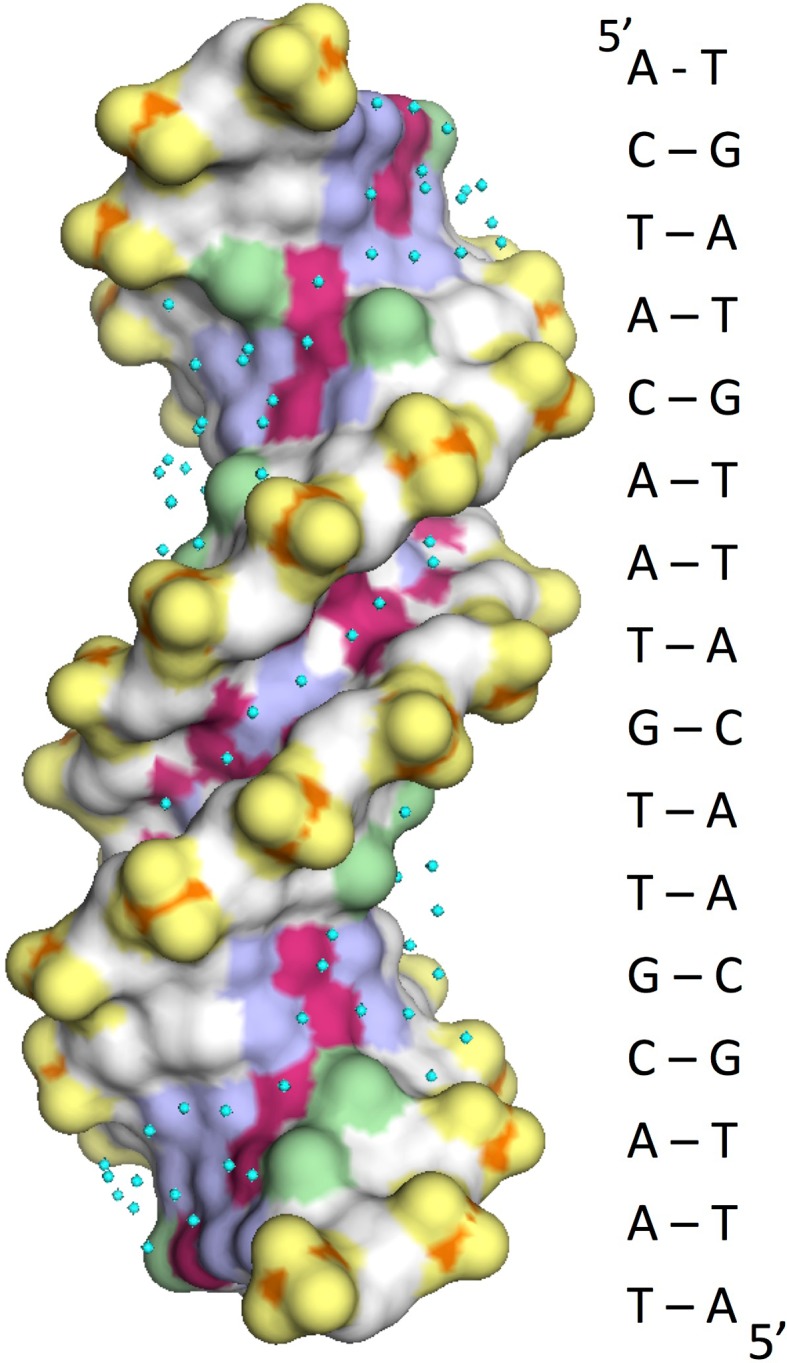
Representation of a 16 bp duplex solved at 1.6 Å resolution (Narayana and Weiss 2009) showing the apolar and polar surface characteristics. Apolar: carbons in white and the methyl groups of T in green. These constitute the walls of both grooves. Polar: red (negative) and blue (positive). These make up the bottom of both grooves. Phosphate groups are separately designated in yellow and water molecules are shown as cyan dots. Note the very regular array of eight waters covering six bp in the central minor groove (five ATs interrupted by a single GC). Water molecules in the major groove are more haphazardly positioned
