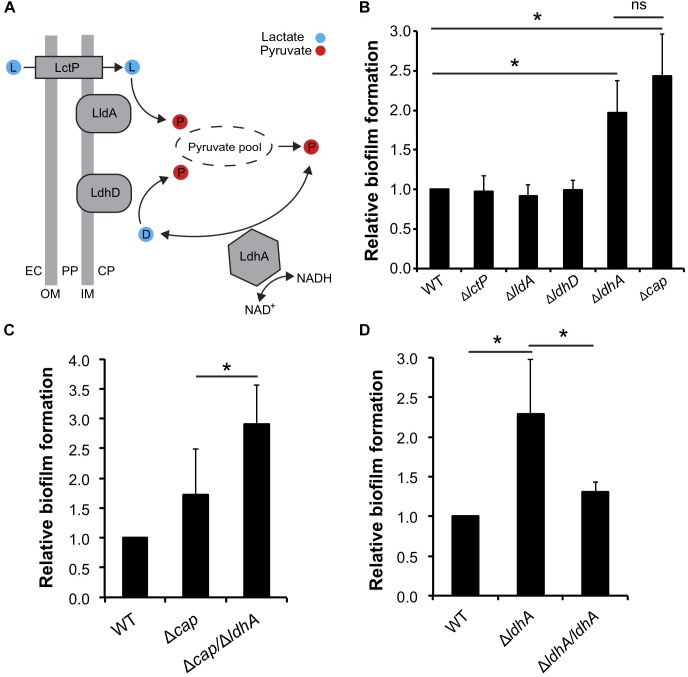
FIGURE 1.
Deletion of ldhA promotes meningococcal biofilm formation in vitro. (A) Predicted role of lactate dehydrogenases (LDHs) in N. meningitidis, adapted from Atack et al. (2014). Abbreviations: LctP, lactate permease; LldA, respiratory L-LDH; LdhD, respiratory D-LDH; LdhA, cytoplasmic NAD+ dependent D-LDH; NAD+, oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; EC, extracellular space; PP, periplasm; CP, cytoplasm; OM, outer membrane; IM, inner membrane. (B) Biofilm formation by the wild-type, ΔlctP, ΔlldA, ΔldhD, and ΔldhA mutant strains. Δcap was used as a positive control. (C) Biofilm formation by the wild-type, Δcap, and ΔcapA/ΔldhA strains. (D) Biofilm formation by the wild-type, ΔldhA, and ΔldhA/ldhA strains. For all biofilm experiments, bacteria were resuspended in GC liquid supplemented with 1% Kellogg’s supplement to an OD600 of 0.05 and grown under static conditions at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 24 h. The biofilm was washed twice in PBS and then stained with crystal violet. After washing two times with PBS, the biofilm was dissolved with acetic acid and quantified by measuring the absorbance at 630 nm. Experiments were performed at least three times in triplicate. The bars represent the means, with error bars representing the standard deviations. ∗p < 0.05. ns, non-significant.