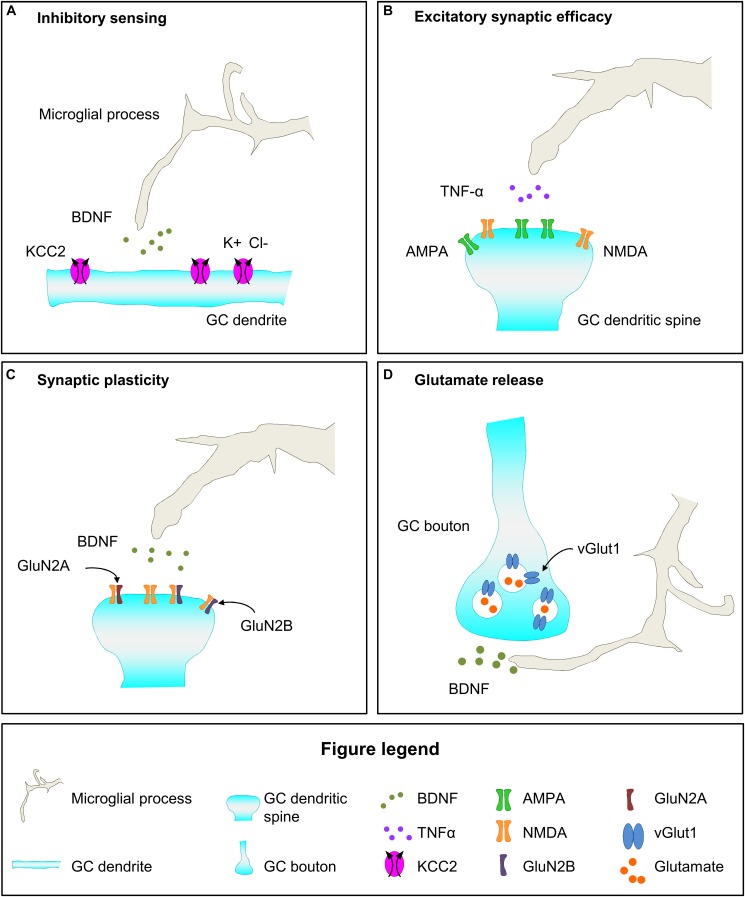
FIGURE 6.
Hypothetical mechanisms of microglial regulation of functional maturation of synapses of newborn GCs. (A) Microglia may secrete BDNF, which upregulates the expression of the cotransporter KCC2 in newborn GCs, and increases their inhibitory sensitivity to GABA. (B) Microglia derived TNF-α may increase synaptic efficacy by increasing the AMPA/NMDA ratio. (C) Microglial BDNF may contribute to the enhanced synaptic plasticity of newborn GCs by raising the proportion of GluN2B subunit in NMDA receptors. (D) Microglia secreted BDNF may increase glutamatergic transmission by upregulating the expression of vGlut1 in presynaptic vesicles. BDNF, brain derived neurotrophic factor; Cl, chloride; GC, granule cell; K, potassium; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; vGlut1, vesicular glutamate transporter 1.