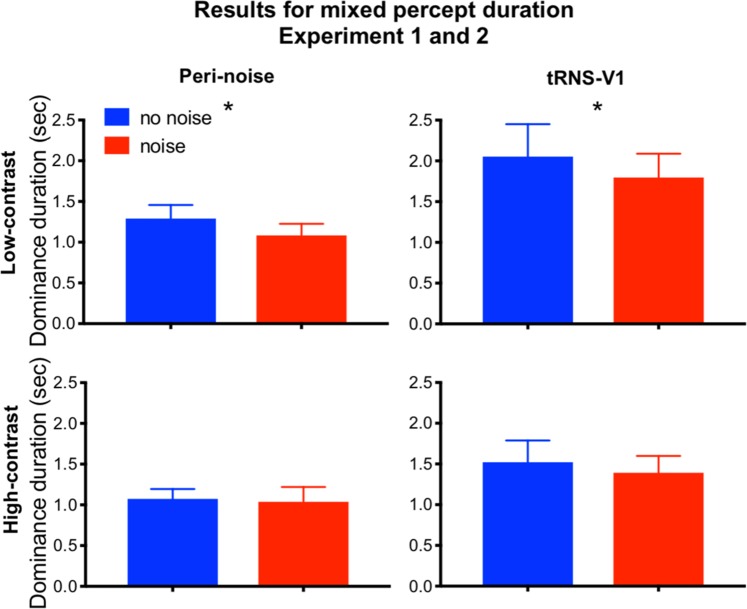
Figure 3.
Behavioural results from Experiments 1 (left) and 2 (right). Adding noise to the visual stimulus significantly reduced the dominance duration of the mixed percept for low contrast visual stimuli by 16%, whereas the dominance duration for the high contrast visual stimuli was reduced by 4%. In Experiment 2 (right) the noise was added to the cortex with tRNS. This resulted in a reduction of 15% in median mixed percept duration. The dominance duration for the high contrast visual stimuli was reduced with 6% There was no significant effect of adding noise on the dominance duration of the exclusive percept. Error bars represent standard errors (s.e.m.).