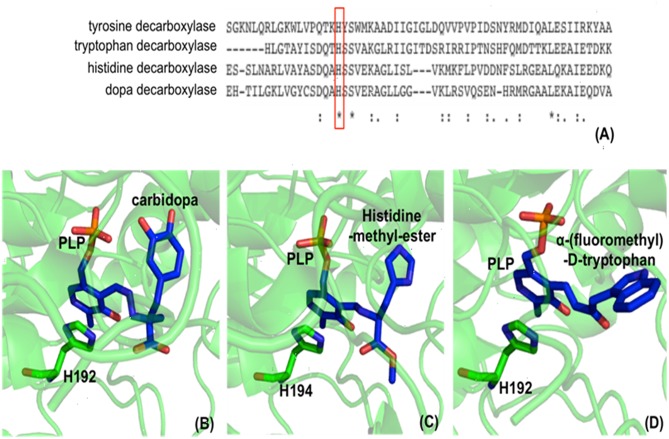
Figure 4.
Partial protein sequence alignment of aromatic amino acid decarboxylases, and the positions of the conserved His residue in aromatic amino acid decarboxylases. The conservation of His192 residue (residue number is from Drosophila melanogaster dopa decarboxylase) in Lactobacillus brevis tyrosine decarboxylase (PDB: 5HSJ, chain A) (Zhu et al., 2016), Ruminococcus Gnavus tryptophan decarboxylase (PDB: 4OBU, chain E) (Williams et al., 2014), Homo sapiens histidine decarboxylase (4E1O_A) (Komori et al., 2012), and Drosophila melanogaster dopa decarboxylase (Accession: NP_724164.1) is shown and is highlighted in red box (A). The dopa decarboxylase complexed with PLP and substrate-like inhibitor carbidopa [PDB: 1JS3 (Burkhard et al., 2001)] (B), the histidine decarboxylase complexed with PLP and substrate analog histidine-methyl-ester [PDB: 4E1O (Komori et al., 2012)] (C), and tryptophan decarboxylase complexed with PLP and substrate analog α-(fluoromethyl)-D-tryptophan [PDB: 4OBV (Williams et al., 2014)] (D) are shown. The external aldimines formed by PLP and substrate analogs are colored in blue and the conserved His residues in each decarboxylase critical for decarboxylation activity are shown in green sticks.