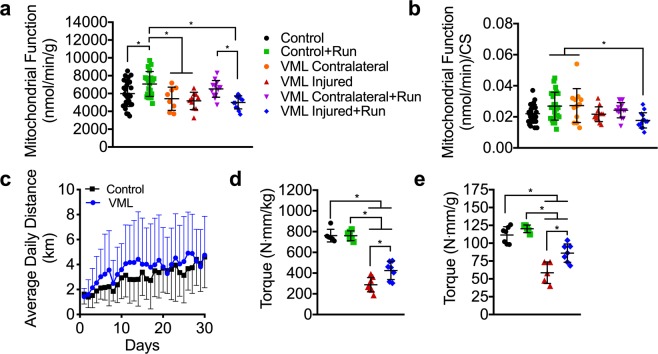
Figure 5.
The effects of VML and voluntary wheel running on muscle strength and oxidative capacity 4 weeks post injury. (a) Mitochondrial respiratory function normalized by grams wet weight of permeabilized muscle fibers (n ≥ 12 permeabilized fiber bundles from n = 6 mice for each condition) did not adapt to exercise training in the VML injured limb. (b) Mitochondrial respiratory function normalized to citrate synthase enzyme activity (see Table 1). (c) Wheel running distance of control and VML injured mice. Peak isometric torque normalized to (d) body mass and (e) plantarflexor mass in the VML injured limb was significantly greater after voluntary wheel running. Data analyzed by one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05. Error bars represent means ± SD.