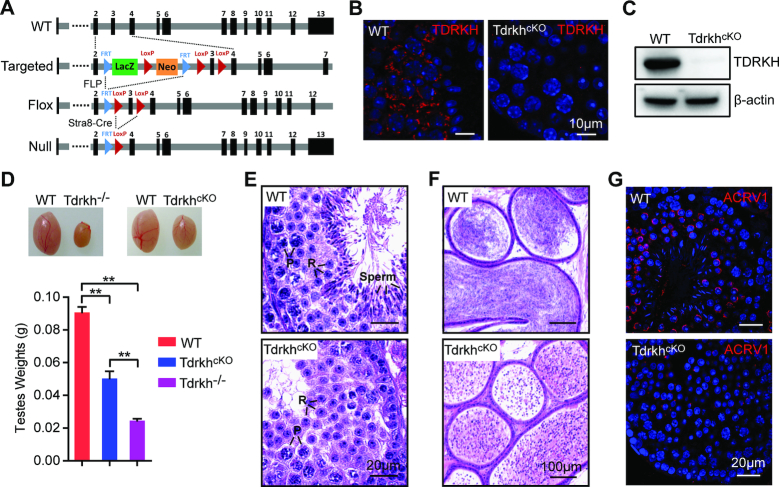
Figure 1.
Loss of TDRKH in postnatal male germ cells causes spermatogenic arrest in mice. (A) A schematic diagram showing the gene targeting strategy for the generation of a Tdrkh conditional allele. Cre-mediated deletion removed the exon3 of Tdrkh and generated a protein null allele. (B) Immunostaining of TDRKH in adult WT and TdrkhcKO testes. DNA was stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Western blotting of TDRKH expression in adult WT and TdrkhcKO testes. β-Actin served as a loading control. (D) Testicular atrophy in TdrkhcKO mice. Testis sizes and weights of adult WT, TdrkhcKO and Tdrkh−/− mice are shown. n = 8. Error bars represent s.e.m. The P-value was calculated using unpaired t-test. **P < 0.01. (E) Spermatogenic arrest in TdrkhcKO testes. Hematoxylin and eosin stained testis sections from adult WT and TdrkhcKO mice are shown. Scale bars, 20 μm. P, pachytene spermatocytes; R, round spermatids; Sperm, spermatozoa. (F) Hematoxylin and eosin stained epididymis sections from adult WT and TdrkhcKO mice are shown. Scale bars, 100 μm. (G) Spermatogenic arrest at the round spermatid stage in TdrkhcKO testes. Co-immunostaining of ACRV1 and γH2AX in stage VII–VIII seminiferous tubule from WT and TdrkhcKO testes. DNA was stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 20 μm.