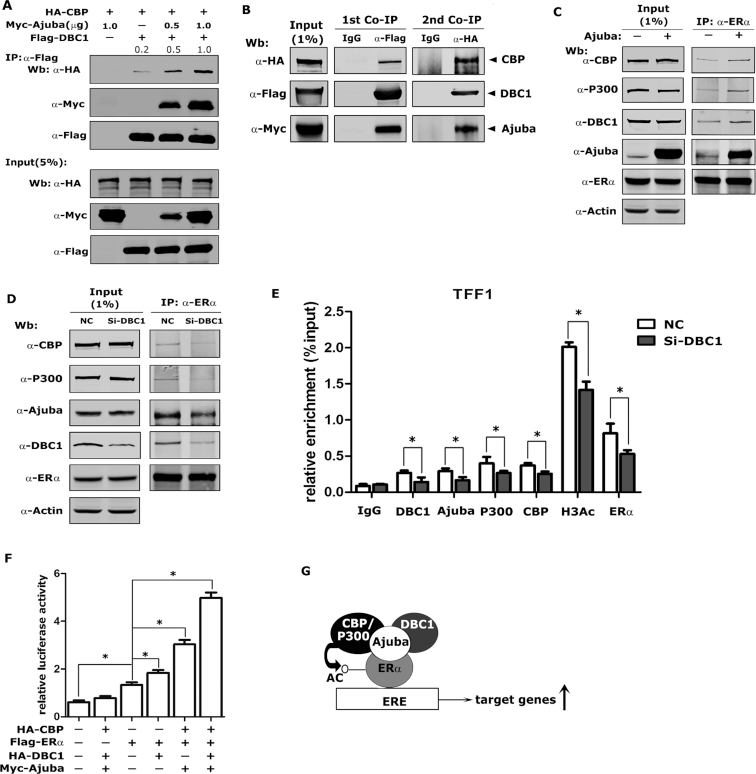
Figure 7.
Ajuba, DBC1 and CBP/p300 forms a ternary complex to enhance ERα target gene transcription. (A) Plasmids were transfected into 293T cells and the Co-IP assay was performed by using Flag-M2 beads (the relative amount of immunoprecipitated HA-CBP was semi-quantified by grayscale analysis and the mean values of the three repeats were labeled). (B) Myc-Ajuba, HA-CBP and Flag-DBC1 plasmids were co-transfected into 293T cells and sequential co-IP assays were performed. The first round co-IP assay was carried out by using Flag antibody or normal IgG and then the 3XFlag-peptides eluted product was subjected to the second round co-IP assay by using HA antibody or normal IgG. (C) The endogenous co-IP assay was performed in T47D-PCDH-Vector or T47D-PCDH-Myc-Ajuba cells by using ERα antibody. (D) siRNA-DBC1 was transfected into T47D cells for 48 h, and the co-IP assay was performed by using ERα antibody. (E) The siRNA-NC or siRNA-DBC1 was transfected into T47D cells and the ChIP assay was performed after the E2-treatment and the results were normalized to input and 5–10% as input (three repeats, * means P < 0.05). (F) TFF1-luciferase reporter assays were performed in 293T cells. Transfected cells were treated with 20 nM E2 for 12 h before harvesting and the value was normalized to β-gal (three repeats, * means P < 0.05). (G) The model of Ajuba regulating ERα transcriptional activity. Ajuba forms a complex with DBC1 and CBP to enhance the acetylation and transactivity of ERα.