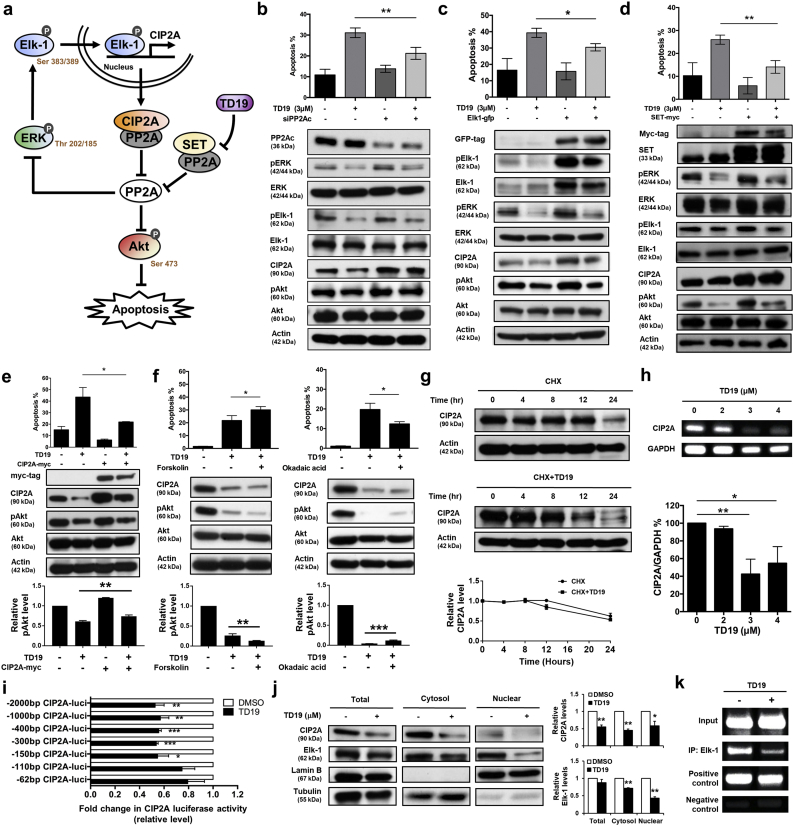
Fig. 5.
Targeting SET disrupts oncogenic CIP2A feedforward loop in TNBC cells.
(a) Illustration of CIP2A/PP2A/pERK/pElk-1 feedforward loop. (b-d) MDA-MB-468 cells were transfected with siRNA against PP2Ac (b), Elk-1- (c) or SET-expressing plasmids (d) for 24 h. Then the cells were treated with TD19 (3 μM) or DMSO. Cells were assayed for sub-G1 analysis (up). Whole-cell lysates were further analyzed by Western blot (down). (e) Ectopic expression of myc-tagged CIP2A reduces the apoptotic effect of TD19 in MDA-MB-468 cells (up). Whole-cell extracts were analyzed by Western blot (middle). The results were quantified (down). (f) Co-treatment of PP2A agonist forskolin enhanced TD19-induced apoptosis. MDA-MB-468 cells were co-treated with DMSO (control) or TD19 (3 μM) and forskolin (40 nM) for 24 h (left). Pretreatment of PP2A inhibitor okadaic acid protected cells from TD19-induced apoptosis. MDA-MB-468 cells were pretreated with or without okadaic acid (20 nM) for 1 h; then washed and treated with DMSO (control) or TD19 (3 μM) for 24 h (right). Cells were assayed for sub-G1 analysis (up). Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot (middle). The results were quantified (down). (g) Limited effect of TD19 on CIP2A protein degradation. MDA-MB-468 cells were treated with 100 μg/milliliter pan-translation inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX) with or without TD19 (2 μM) for the indicated period of time, then the stability of CIP2A protein in whole-cell lysates was assessed by Western blot (up). The results were quantified (down). (h) TD19 inhibited CIP2A transcription. MDA-MB-468 cells were treated with TD19 at 0, 2, 3 and 4 μM for 24 h; then RNA was isolated for RT-PCR analysis. (i) Promoters with different lengths of deletion were constructed. Followed by transfecting with the mutant clone or the wide-type promoter for 24 h, MDA-MB-468 cells were subsequently exposed to TD19 (3 μM) or DMSO for 24 h. Cell lysates were then assayed for dual luciferase activity. (j) TD19 decreased Elk-1 translocation from the cytosol to the nucleus. Nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were prepared from MDA-MB-468 cells treated with TD19 (3 μM) or DMSO for 24 h. Cell lysates were Western blotted for CIP2A and Elk-1. Lamin B and Tubulin were used as a loading control (up). The results were quantified (down). (k) TD19 disturbed binding of Elk-1 to the CIP2A promoter region. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays of the CIP2A promoter were performed. Soluble chromatin was immunoprecipitated with Elk-1 or IgG (negative control, NC) antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to PCR with primer pairs specific to the CIP2A promoter (−139 to −16 nt). Anti-RNA polymerase II antibody and GAPDH primers were used as a positive control for the assay technique and reagent integrity. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Columns, mean (N = 3); bars, SD. Student's t-test, *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.