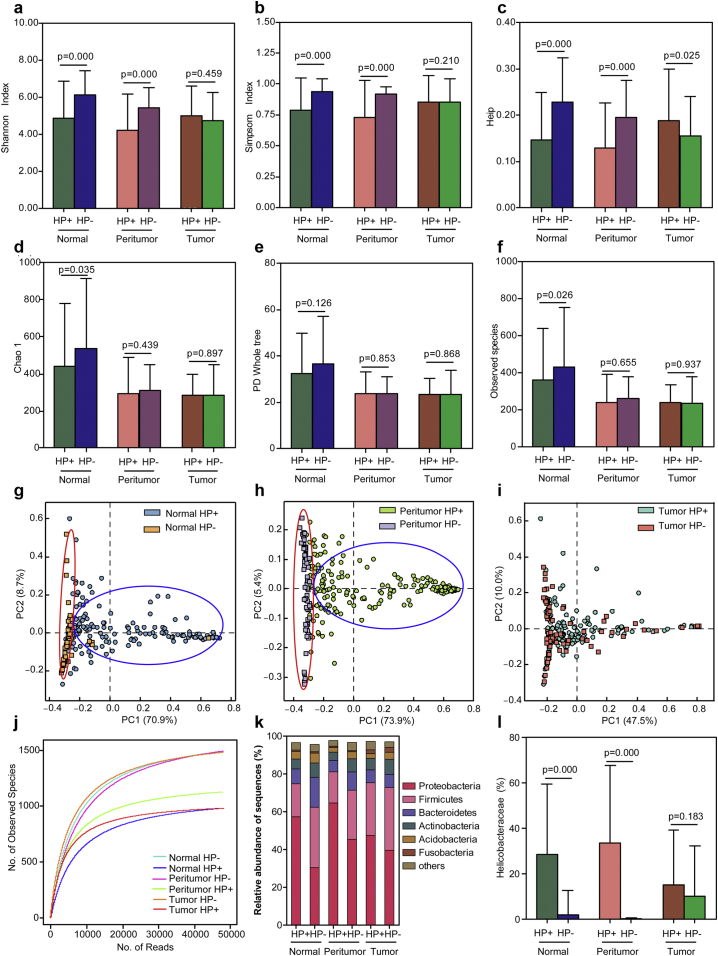
Fig. 5.
Altered gastric microbiota in the three stomach microhabitats influenced by Helicobacter pylori infection (HPI). HPI influenced the diversity indices of gastric microbiota in different stomach microhabitats such as Shannon (a), Simpson (b), Heip evenness (c), and the richness indices such as Chao 1 (d), PD whole tree (e) and observed species (f). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. Unpaired t-tests (two-tailed) were used to analyse variation between HP+ and HP− groups in the three stomach microhabitats. Plots of principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of the gastric microbiota influenced by HPI in normal microhabitats (g), peritumoral microhabitats (h) and tumoral microhabitats (i) based on the unweighted UniFrac metric. Rarefaction analysis of the gastric microbiota from HP+ and HP− groups in three stomach microhabitats (j). Taxonomic differences between the gastric microbiota of HP+ and HP− groups in the three microhabitats at the phylum level (k). The different relative abundance of HP in histopathological HP+ and HP− groups in the three microhabitats (l). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. Mann-Whitney U tests were used to analyse variation between the HP+ and HP− groups in the three stomach microhabitats.